A connection to the edge network has been established. Mobile communication: what is EDGE
EDGE technology is the next step in the development of GSM networks. The purpose of the introduction of the new technology is to increase the data transfer rate and more efficient use of the radio frequency spectrum. With the advent of EDGE in phase 2+ GSM networks, existing GPRS and HSCSD parameters are significantly improved due to changes in signal transmission at the physical layer (modulation and coding) and new radio algorithms for data transmission. The GPRS and HSCS D technologies themselves do not change and can work in parallel with EDG E. Along with the abbreviation EDGE, you can also find the term EGPRS (Enhanced GPRS - “improved” GPRS), which indicates the use of the GPRS service with the new EDGE physical layer. Further, we will consider EDGE only in relation to GPRS, since HSCSD technology has not been widely used in Russia.
The theoretical data rate limit in the radio channel when using EGPRS is 473.6 kbaud, while with GPRS it is only 160 kbaud. High speeds are achieved thanks to a new modulation method and the use of a modified error-tolerant radio signal transmission method. In addition, the changes affected the algorithms for adapting to the channel quality.
Based on the above, we can conclude that EDGE is an addition to GPRS and cannot exist separately. From the consumer's point of view, GPRS expands the capabilities of the GSM network, while EDGE improves the technical parameters of GPRS.
With regard to the infrastructure of the GSM network, EGPR S requires changes to be made to the base stations. In this case, the existing core of the GSM infrastructure is used, and the introduction of EDGE means only the installation of additional equipment (Fig. 1).
Rice. one.
EDGE Options
The table shows the main technical characteristics of GPRS and EDGE technologies.
Table 1.
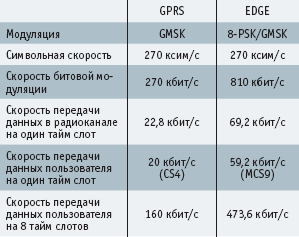
As you can see from the table, EDGE can transfer three times more data than GPRS in the same time period. The difference between the radio data rate and the actual user data rate is due to the fact that overhead data is added to the user data block in the form of a packet header during transmission over the radio channel. This often leads to confusion when determining the throughput of GPRS and EGPRS, since different speed indicators are found in publications. In connection with EDGE technology, the figure 384 kbps is more common: the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) defines this speed in accordance with the requirements of the IMT-2000 (International Mobile Telecommunications) standard, which involves the use of eight time slots with a speed of 48 kbps each.
New type of modulation
When transmitting data in GPRS mode, Gaussian keying with a minimum frequency shift GMSK - Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying (Fig. 2), which is a kind of phase modulation, is used. When a "0" or "1" bit is transmitted, the phase of the signal is positively or negatively incremented. Each transmitted symbol contains one bit of information, that is, each phase shift represents one bit. To achieve a higher data rate in one time interval (in one time slot), it is necessary to change the modulation method.

Rice. 2.
EDGE was designed to use the same frequency grid, channel widths, channel coding techniques, and existing mechanisms and functions used by GPRS and HSCSD. For EDG E, 8PSK (8-Phase Shift Keying) was chosen, which satisfies all these conditions. In terms of adjacent channel interference, 8PSK has the same quality parameters as GMSK. This allows EDGE channels to be integrated into an existing frequency plan and new EDGE channels to be assigned in the same order as normal GSM channels.
8PSK is a linear modulation technique in which 3 bits of information correspond to one transmitted symbol. The symbol rate (or the number of symbols transmitted per unit of time) remains the same as in GMSK, but each symbol carries information in 3 instead of 1 bits. Therefore, the data transfer rate is increased by 3 times. The phase distance between symbols in 8PSK is smaller than in GMSK, which increases the risk of a symbol recognition error by the receiver. With a good signal-to-noise ratio, this is not a problem. Error correction codes should be used to successfully operate in poor radio conditions. Only when the radio signal is very weak is GMSK modulation superior to 8PSK. In order to be able to operate efficiently at any signal-to-noise ratio, EDGE coding schemes use both types of modulation.
Coding schemes and packetization
Four coding schemes are defined for GPRS: CS1-CS4. Each contains a different number of correction bits, optimizing each coding scheme for a certain quality of the radio link. EGPRS uses nine coding schemes, which are designated MCS1-MSC9. The lower four circuits use GMSK modulation and are designed to operate at the worst signal-to-noise ratio. The MSC5-MSC9 schemes use 8PSK modulation. On fig. 3 shows the maximum data rates achievable using different coding schemes. A GPRS user can get a data rate limit of 20 kbaud, while the EGPRS rate increases up to 59.2 kbaud as the quality of the radio link improves (closer to the base station).

Rice. 3.
Although the CS1-CS4 and MSC 1-MSC4 schemes use the same GMSK modulation, the EGPRS radio packets have a different header length and payload size. This allows the coding scheme to be changed on the fly to retransmit a packet. If a packet with a higher coding scheme (with less noise immunity) is received with an error, then it can be resent using a coding scheme of a smaller number (with greater noise immunity) to compensate for the degraded radio link parameters. Transmission with a different coding scheme (resegmentation) requires changing the number of useful bits in the radio message. GPRS does not provide such a possibility, so GPRS and EGPRS coding schemes have different efficiency.
In GPRS, packet repetition is possible only with the original coding scheme, even if this coding scheme has ceased to be optimal due to the deterioration of the radio link quality. Consider the packet retransmission scheme as an example (Fig. 4).

A. The GPRS terminal receives data from the base station. Based on the previous link quality report, the base station controller decides to send the next block of data (numbers 1 to 4) with the CS3 coding scheme. During transmission, the state of the radio link deteriorated (signal-to-noise ratio decreased), as a result, packets 2 and 3 were received with an error. After transmitting a group of packets, the base station requests a new report - an assessment of the quality of the radio link.
b. The GPRS terminal sends information about incorrectly delivered packets to the base station along with information about the quality of the radio link (in the acknowledgment report).
FROM. Taking into account the degradation of communication quality, the adaptation algorithm selects a new, more noise-resistant CS1 coding scheme for transmitting packets 5 and 6. However, due to the impossibility of resegmentation in GPRS, retransmission of packets 2 and 3 will occur with the same CS3 coding scheme, which significantly increases the risk of incorrect reception these packets by the GPRS terminal.
The GPRS adaptation algorithm requires a very careful choice of coding scheme to avoid, as far as possible, retransmission of packets. With resegmentation, EGPRS can use a more efficient encoding scheme selection method, since the probability of packet delivery during retransmission is much higher.
Table 2. Coding scheme group

Packet Addressing
When transmitting a block of packets over a radio channel, the packets within the block are numbered from 1 to 128. This identification number is included in the header of each packet. In this case, the number of packets in a block transmitted to a specific GPRS terminal should not exceed 64. A situation may arise when the number of a retransmitted packet coincides with the number of a new packet in the queue. In this case, you have to retransmit the entire block as a whole. In EGPRS, the packet address space is increased to 2048, and the sliding window size is 1024 (the maximum number of packets in one block), which greatly reduces the likelihood of such collisions. Reducing retransmissions at the RLC (Radio Link Control) level ultimately leads to an increase in throughput (Fig. 5).

Measurement of the quality of the radio channel
The quality of radio link communication in GPRS is assessed by measuring the level of the received signal, evaluating the BER parameter (bit error rate - the relative number of incorrectly received bits), etc. Performing this assessment takes a certain amount of time from the GPRS terminal, which, in principle, is not plays a big role in the constant use of one coding scheme. With packet data switching, it is necessary to quickly monitor the quality of the radio link in order to quickly change the coding scheme depending on the state of the radio air. The channel quality estimation procedure in GPRS can only be performed twice within a 240-ms period. This makes it difficult to quickly select the correct coding scheme. In EGPRS, measurements are made at each reception by estimating the bit error probability (BEP). Based on the data of each transmission, the BEP parameter reflects the current signal-to-noise ratio and the temporal dispersion of the signal. As a result of this approach, the estimation of the transmission channel quality parameters turns out to be sufficiently accurate even for a short measured period. This determines the higher efficiency of the adaptation scheme compared to GPRS.
Link monitoring functions and enhanced redundancy
To ensure the maximum transmission rate under the conditions of the existing radio channel quality, EGPRS uses the following mechanisms:
- Adaptation to channel quality. Based on the link quality measurements in data transmission (both to and from the mobile terminal), the adaptation algorithm selects a new coding scheme for the next sequence of packets. Coding schemes are grouped into three families - A, B and C. A new coding scheme is selected from the same family as the previous one (Fig. 5).
- Increased code redundancy. Increased redundancy (Incremental Redundancy) is used for older coding schemes in cases where, instead of analyzing the parameters of the radio link and changing the coding scheme, sending additional information is used in subsequent transmissions. If errors occur during the reception of a packet, redundant information may be sent in the next packet to help correct previous incorrectly received bits. This procedure can be repeated until the information in the previously received packet is completely restored.
In Russia, the Big Three operators already provide EDGE services in several districts of Moscow and in a number of regions of the country. The introduction of EDGE occurs gradually, as the equipment of base stations is updated. By the end of 2005 MegaFon plans to cover about 500 base stations with EDGE technology. VimpelCom is going to introduce EDGE fragmentarily in Moscow within the Moscow Ring Road (in areas with increased GPRS traffic), and throughout Russia - in all regions by the end of 2006 - beginning of 2007. MTS states that "the work is being carried out very intensively: EDGE coverage in the Moscow region is expanding almost daily."
Literature
- EDGE. Introduction of high-speed data in GSM/GPRS networks (www.ericsson.com/products/white_papers_pdf/edge_wp_technical.pdf). /link lost/
- Materials of the Mobile Forum website (http://mforum.ru/news/article/01-5533.htm). /link lost/
The article will help you figure out what the Edge option on your phone means.
If you use the Internet through your phone, then you may have a question: what does Edge mean on a phone? This option helps to increase the speed of information transfer in GSM networks. Your mobile operator must support this option in order for you to use it.
A large load on network lines, the level of data supply, the amount of free information in the network database - all this affects the work of Edge. But using this option has its advantages compared to gprs:
- The highest speed of information transfer.
- The ability to access the global network from anywhere in your locality.

At present, such a seemingly modern, but already a little outdated option, is gradually being squeezed out of the global mobile communications market. The evolution of cellular standards is moving forward. This is necessary for consumers who live in the rhythm of a big city. After all, Internet access is needed not only at home or at work, but also in the subway or in the minibus on the way home.
Users often ask the question: what does Edge mean in Samsung? In the Samsung Galaxy S7 phone, the edge prefix indicates a curved screen. This version is much more popular than the previous model.
It's rare to find an Edge user on a phone these days. This technology is being replaced by 3G and 4G networks. They have an even higher data transfer rate and a better signal.
Video: SPEEDTEST WIFI VS 2G/EDGE VS 3G VS 4G/LTE
World telecommunications are experiencing a powerful leap forward for about 80 years already. A lot of time has passed since the appearance of the first means of communication. Now, we have the opportunity to communicate not only using telephone networks, but also Internet telephony, which, under an hour, is several times cheaper than conventional types of communication. Of course, the cheapest form of communication remains communication with a person during a conversation on one space-time interval. Let's talk about new technologies. What is edge and what is it eaten with? So:
edge. What it is?
The edge system first appeared in North America. It was then, in 2004, that the Americans had the first add-on to the GSM mobile communication system.
What is edge? This is a new communication system that works in mobile communication. It is used in GSM networks. edge is referred to as a digital wireless data transmission system over long distances.
So, as already mentioned, edge appeared in 2004 in North America. Many operators, however, were very skeptical about introducing edge technologies into their communications system. Many thought the next step in their development was the use of UMTS networks. As they worked, companies providing mobile services realized that the creation of UMTS networks is an expensive and unprofitable undertaking, in connection with this, many mobile operators revised their positions and turned to edge technology. Gradually, the influence and use of edge spread to the European part of the world. In Russia, the "big three" operators started using edge by the end of 2004. People started using edge on their phones. The "Big Three" mobile operators include Megafon, Beeline and MTS.
Thus, we can conclude that the development of edge technology is moving forward by leaps and bounds. It is important to note that in our time types of communication of the third and fourth generations are receiving great development. For example, Apple is already releasing phones based on 4G technology, that is, fourth-generation technologies. When we talk about edge, we mean technologies like 2G and 2.5G. This is the second and second and a half generation of communication. It makes no sense to specifically mention that edge will gradually be forced out of the market. But this is a natural course of time, which requires a quick response of manufacturers and scientists to all new needs and requests of users around the world. Despite the above facts, edge has firmly established itself as a leader among mobile communication technologies. Only very recently has a truly powerful competitor to edge emerged, namely the Apple iPhone 3G. It quickly gained popularity among users around the world and is gaining momentum by leaps and bounds. What will happen next? We'll see very soon.
It is still used in many banking systems and is very resistant to hacking and data leakage. Unfortunately, in Russia it is very expensive, but this does not negate its degree of demand for a certain circle of people.
GPRS technology is a "packet" technology, it collects all information into conventional units (packets) and transmits them at a speed of 56 before 114 kbps. This provides access to the Internet, downloading melodies, pictures, games, sending short multimedia messages (MMS), communication by ICQ or mail.
EDGE transfers data about three times faster than GPRS - in theory, EDGE is capable of supporting file transfer rates up to 474 kbps, while the peak value of GPRS is 171,2 kbps. The numbers speak for themselves, although in practice the speed indicators are much more modest.
(from the English generation third - the third generation) - third-generation mobile GSM communication technology, which combines both voice communication capabilities and high-speed mobile Internet access. The third generation of radio communication differs from previous versions in its increased speed of operation, transmitting data at speeds up to 3,6 Mbps This makes it possible to use all the advantages of high-speed Internet on a mobile device: watch movies and TV programs on-line, organize mobile videotelephone communications, download large amounts of data, etc.
Step 1. We connect the GPRS/EDGE/3G service
All operators have GPRS / EDGE / Internet service initially connected. But in some cases, the service needs to be connected independently. The speed of Internet access depends on the device that the user uses at a certain moment and on the coverage area in which he is. The coverage is much inferior to GPRS / EDGE, but at the same time it gives a huge gain in network connection speed.
Various methods can be used to disconnect any mobile device from the Edge network, although some of them are characterized by general principles of action that can be used on all cell phone models. Let's figure it out: what is the network and how can you turn it off on your smartphone?
What is EDGE
The icon showing the letter E, usually located at the top of the mobile phone screen, indicates that your mobile device is located in the coverage area of the EGPRS network. Most models of modern mobile devices support different networks, among which the main standard is GSM, as well as another commonly used option is the UMTS network. When the E symbol appears on the screen, you can be sure that an access point for your mobile device has opened, although this does not mean that this EGPRS network can be used for data exchange. You must find out exactly what parameters are indicated in the “access point” line by opening the settings of your mobile phone. The WAP GPRS or GPRS Internet.nw settings allow you to use this particular network for data transfer and with this option the E icon is only a potential option to use the EGPRS network.How to disable EDGE on your phone
The easiest method used to disconnect a device from the Edge network, and recommended by cell phone manufacturers, is to turn the device off and then on again. You can also use the reboot of the mobile device.If you are sure that a mobile phone that runs on Android OS uses an Edge connection in order to make an active Internet connection in order to check for updates, on some forums it is advised to use a specialized service code “*#4777*8665#” to call Attach Mode Settings menu. After that, you need to specify the GPRS detach command and reboot the mobile device.
Apple does not provide an explicit option to disable the GPRS/Edge transmission protocol, although depending on the conditions in which roaming is used, enabling this feature may cost the subscriber too much. To disable this feature, you must use the tweak to change the APN values in the iPhone device configuration. To do this, you need to open “Settings” by going to the main page of the device, and go to the “General” category. Next, you must click on the “network” link and select the Edge category. Then you need to print the sign. (dot) in the “APN address” field after entering the address. After you have completed the steps, if you try to use this function, a message box should appear showing that this service is disabled and data transfer over it is not possible.