Motherboard detail
Hello friends.
In this article, we will take a closer look at the motherboard and everything connected with it. Let's figure out what a socket, chipset is, what internal connectors exist on the motherboard. Let's find out what they are used for. We will learn to understand the differences between motherboards and choose them correctly for your computer.
Motherboards and what they eat with.
The motherboard (English motherboard or mainboard) is the basis of the computer to which all other elements of the PC are connected. It is a textolite multilayer printed circuit board on which various radio elements and connectors are installed. Serves as an intermediary in the interaction of various nodes of the computer.
Despite the fact that the entire configuration is assembled on the motherboard, it is still not the main element of the system. It should be chosen based on the characteristics of the rest of the equipment we need.
Motherboards may differ from each other by manufacturer, set of additional features, differences in form factor, chipset, socket, set of external and internal connectors.
Form Factor
The form factor of the motherboard is a standard that determines the dimensions of the board, the places where it is attached to the case, the places and number of connectors, and the type of power supply to be connected. These specifications are not mandatory, but most manufacturers try to comply with them for the sake of compatibility with other equipment. At the moment, these standards are used only in PCs and do not apply to other computer equipment such as laptops or tablets.
There are a large number of form factors, but today we will not consider them all in detail. Let's focus on the 3 most commonly used: ATX, Mini-ATX and Micro-ATX. Their main difference is in the size and PCI slots.
The form factor is selected based on the need for connectors for the connected equipment. So, for example, a Mini-ATX motherboard will suffice for an office computer. It will be smaller and cheaper than the full size. In turn, a full-size ATX motherboard is the preferred choice when building a gaming PC or PC for graphics. It accommodates a larger number of connectors with which you can connect additional equipment. For example, additional RAM sticks, more hard drives, 2 video cards, etc.
Remember, when choosing the form factor of the motherboard, do not forget about the dimensions of the case. When assembling, it will be extremely unpleasant to suddenly discover that the mat. The board does not fit into the case.
The processor socket is the connection between the processor and the motherboard. The socket is one of the main parameters when choosing a motherboard. It must be the same as on the processor.
Socket connectors are divided into 2 types, depending on the manufacturer of the processor. For Intel processors, the presence of the letters LGA and a digital designation (LGA1155 or LGA775) is specific in the name. AMD is characterized by a one- or two-letter designation with a digital prefix of 1 or 2 digits, possibly with a + symbol (AM3+ or FM2).

A chipset is a chip or group of chips that coordinates connected equipment.
The chipset is a very important element of the motherboard. The maximum speed of operation and the number of connectors on the board depend on it. Most often, the chipset is covered by a heatsink. They are also divided by manufacturer, the most common Intel chipsets at the moment are 7 series chips (Z77 and H77), and AMD chipsets are represented by 900 series (990FX, 990X, 970).
The difference in chipsets affects the price of the motherboard quite a lot. Also, more powerful chipsets consume more electricity and generate more heat, therefore, they are more demanding on cooling. For office computers, a more powerful chipset will be a burden, but for gaming machines it is necessary. On cheaper chipsets, the connected equipment will not be able to fully reveal itself and work with maximum performance.

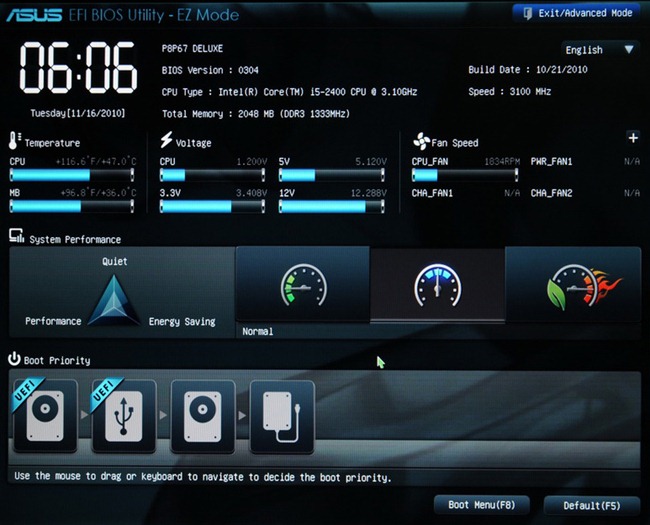
An important component of motherboards is its control system. This is the BIOS. In newer UEFI boards. UEFI is a more advanced version of the BIOS. It has a more informative graphical interface and can display not only sets of startup options, but also the status of the system as a whole and individual elements, such as temperature, occupied connectors, or the amount of RAM.
Internal connectors.
Internal connectors are used to connect equipment that remains inside the system unit. For example RAM or hard drive. Consider in detail the main connectors of the motherboard:
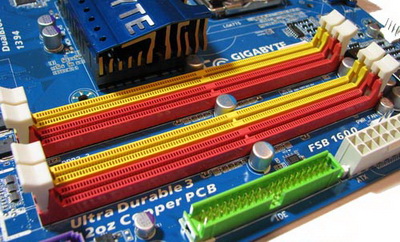
RAM slots.
RAM is installed in specially designed slots. The number of slots ranges from 1 to 32. Most often there are boards with two or four slots for RAM. Modern memory strips come in 2 types: DDR3 and DDR4. The latter has lower power consumption and higher data transfer rate (frequency). If there are 4 or more slots, then the slots work in pairs. They are also marked in pairs on the motherboard. Pairs are marked with different colors. To increase performance, you should buy paired memory sticks and connect them in pairs to the connectors.
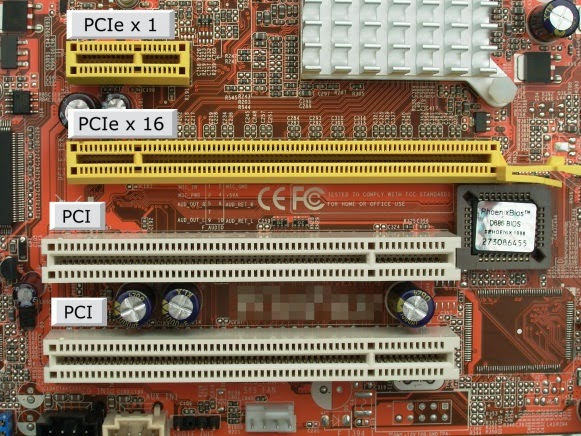
PCI slots.
These connectors are found in 3 main form factors: PCI, PCI-Express x1 and PCI-Express x16. The number of these slots may vary depending on the motherboard type and manufacturer.
PCI-Express x16 slots are designed for equipment with high data transfer rates. Most often used to connect various video cards.
PCI-Express x1 connectors are used to connect low speed equipment such as additional USB controllers or TV tuners.
PCI slots are more outdated than the previous ones, but are still used in modern computers. It has a lower speed, but is still actively used for various peripherals such as network or sound cards.
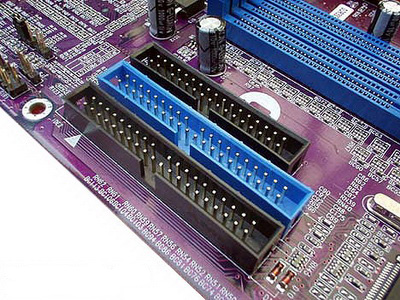
SATA connectors.
This type of bus is most often used to connect hard drives and optical drives (CD, DVD, Bluray drives). These connectors come in 3 main revisions: SATA1, SATA2 and SATA3. Each next generation is twice as fast as the previous one. They are backward compatible and allow you to connect to each other without any problems, but the speed will be considered in this case according to the slowest one. Most often, motherboards combine the presence of these connectors and separate their types in different colors.

These are outdated connectors that were previously used to connect hard drives, CD-DVD drives and Floppy drives. At the moment, they are completely outdated and have been supplanted by SATA connectors.
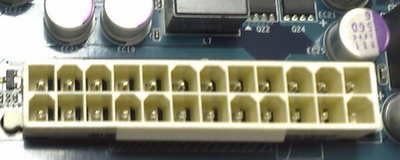
Power connectors.
Rectified voltage is supplied to the motherboard through the power connectors. For the operation of different elements of the computer, different voltages are needed, so there are so many pins in this connector. The most common are 24 pin connectors. Also often there are additional 4- or 6-pin processor power connectors.
Cooler connectors.
To connect cooling systems, small 2 or 4 pin power connectors are used. The 4-pin connectors have speed sensors and are controlled by PWM (Pulse Width Modulation). Most often, the connectors on the motherboard can be from 1 to 4. The main cooler is used to connect the CPU cooling, its power connector is labeled cpu_fun.

Other internal connectors.
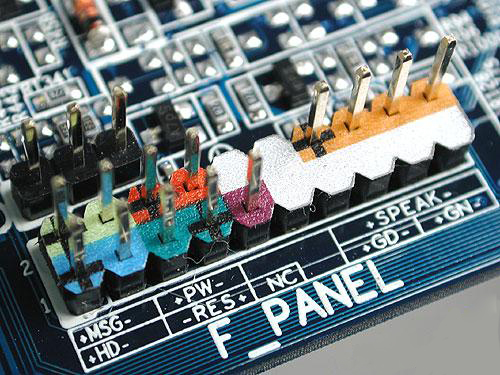
Also, depending on the type and class of the motherboard, it may have additional connectors. The main group of these connectors is located at the bottom of the motherboard. There are connectors for connecting the case buttons on / off and rebooting the PC, outputs to the front audio connectors and additional USB + monitoring systems (processor load, interaction with the hard drive). The description of connecting these connectors is printed on the motherboard next to them or described in more detail in the instructions for the motherboard.