ReFS file system. Benefits and prospects
The way something is stored usually always implies some kind of orderliness, but if in human life it is not a prerequisite, then in the world of computers, storing data without it is almost impossible. This orderliness is reflected in the file system - a concept familiar to most users of various electronic devices and operating systems.
The file system can be compared to some kind of markup that determines how, where and in what way each byte should be written to the media. The first file systems that appeared at the dawn of the electronic era were very imperfect, such as Minix, a file system that has a lot of limitations and is used in the Minix operating system of the same name, which later became the prototype of the Linux kernel.
But time passed, new file systems appeared, more advanced and stable. Today, the most popular of them, at least among Windows users, is NTFS, which replaced FAT32, which is now used only in small flash drives and has many drawbacks, of which the most significant is the inability to write files larger than 4 GB. However, NTFS is not without them. So, according to many experts, it lacks economy, performance and stability, therefore, it's time to think about creating an even more advanced file system that can meet the growing demands from first server, and then client systems.
And so, in 2012, Microsoft developers introduced the Resilient File System, or ReFS for short, a recoverable file system positioned as an alternative to NTFS, and in the future, perhaps its replacement. In fact, ReFS is a continuation of the development of NTFS, from which it was decided to remove everything superfluous that did not become in demand, but instead add new features.
New in Resilient File System:
- Architecture using feature (storage spaces)
- High fault tolerance. File system errors that led to data loss in NTFS will be minimized in ReFS
- Isolation of damaged areas. In case of damage to areas of the file system, access to the recorded data can be obtained from under a running Windows
- Proactive error correction. Automatic scanning of volumes for damage and application of preventive data recovery measures
- Automatic recovery of subfolders and related files when metadata is corrupted
- Using Redundant Writes to Improve Fault Tolerance
- The maximum volume size in ReFS can reach 402 EB versus 18.4 EB in NTFS
- On a ReFS formatted file, you can write a file of 18.3 EB
- The number of files in one folder is 18 trillion. vs. 4.3 billion in NTFS
- The length of the filename and path to it is 32767 versus 255 in NTFS
What will be removed:
- Data compression support
- Data encryption using EFS technology
- Extended file attributes
- Hard links
- Disk quotas
- Support for short names and object IDs
- Ability to change the cluster size (remains questionable)
What will be inherited from NTFS:
- Access Control Lists (ACLs)
- Creating volume snapshots
- Mount points
- Reparse points
- BitLocker encryption
- Creating and Using Symbolic Links
- Recording all changes that occur in the file system (USN journal)
ReFS is currently in its early testing phase, however, computer geeks can begin to appreciate the benefits of ReFS right now, and on a Windows 8.1 or 10 client system. To do this, you will need to perform the following registry tweak:
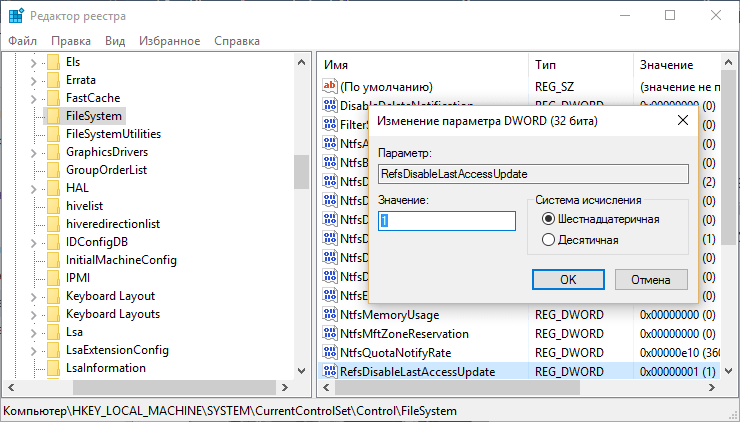
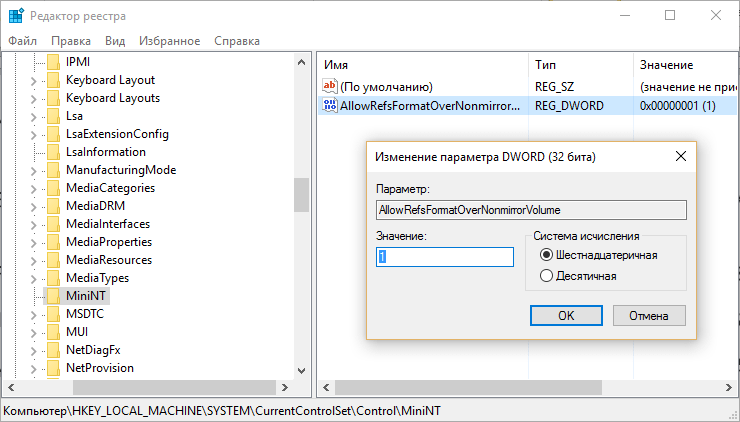
However, using ReFS on a permanent basis is not recommended. Firstly, the system is not yet fully developed, secondly, there is no possibility of converting to ReFS and vice versa by third-party programs, and thirdly, if you accidentally lose or delete files from a partition formatted in ReFS, there will be nothing to restore them, since programs There are no data recovery tools that work with this file system yet.
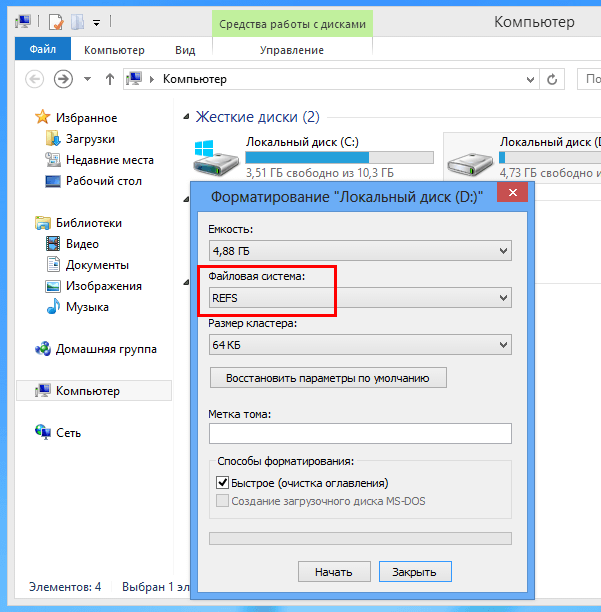
Should we expect the implementation of ReFS in the near future? With a greater degree of certainty, we can say that it is not. If it gets practical use, then first on server systems, which will also not happen soon, but users of client Windows will have to wait after that for at least another five years. Suffice it to recall the implementation of NTFS on client systems, and then it took Microsoft seven years to do this. Well, and most importantly, there is simply no special need for ReFS. When zettabyte disks appear on desktop computers, then, perhaps, the finest hour will come for ReFS, but for now we just have to be patient and wait.
Have a great day!