The hard drive is
First production hard drive with a capacity of 16 kb was released by IBM back in 1973, and contained 30 magnetic cylinders with 30 tracks each. Sharp-tongued developers caught the similarity of these numbers with the brand "30/30", which corresponds to the name of the weapon - "Winchester".
is a hard disk drive.
The main element of hard disk drives (HDD - Hard Disk Drive) is a few rigid aluminum or glass plates of a round shape - disks. The surface of such a disk is covered with a thin layer of a substance that is able to retain residual magnetization after exposure to an external magnetic field. This layer is called the working or magnetic layer and recorded data is stored on it. The drive consists of such elements.
- Discs with a rotating drive that are mounted on a common vertical axis.
- Heads of reading / writing information with their own drive.
The main quality criterion is surface recording density. The modern indicator is 60-80 GB / plate.
Any hard drive consists of three main blocks. So let's take a look at the ingredients hard disk structure.
First block- in fact, the information storage itself is one or more glass (or metal) disks. The disk structure looks like this: the magnetic surface of each disk is divided into concentric " tracks (track)", which, in turn, are divided into segments - sectors. Along with tracks that have their own number, and sectors, there are cylinders. A cylinder is a collection of all tracks that coincide with each other vertically on all working surfaces. Thus, to find out how many cylinders a hard drive contains, you simply need to multiply the number of tracks by the total number of working surfaces. With low-level disk formatting, which is performed at the manufacturing plant, at the beginning and at the end of each sector, areas are created that contain information about their numbers and other (service information). The sector size is 571 bytes, of which 512 bytes are reserved for useful data for the user, the others are for the header (header) or prefix, which determines the beginning and number of the sector and the end (trailer) or suffix, where the checksum necessary for checking disk integrity.
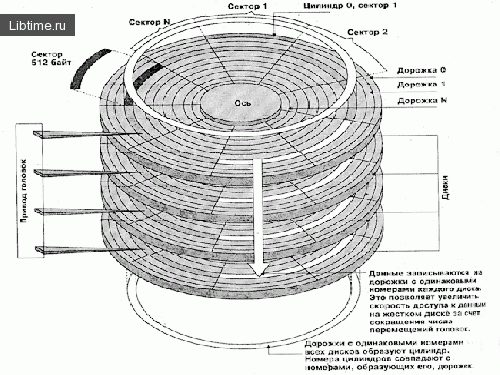
Second block- the mechanics of the hard disk, which is responsible for the rotation of the array of "pancakes" and the precise positioning of the system of reading heads. Each working surface of the hard disk corresponds to one reading head, and they are placed vertically in an exact column. This means that at any given time, all heads are on tracks with the same number. That is, they work within the same cylinder.
Third block includes electronic stuffing - microcircuits responsible for data processing, correction of possible errors and control of the mechanical part, as well as cache memory microcircuits.
Cluster is the smallest area of the disk that is allocated for a file or part of it. Each file occupies disk space equal to an integer number of clusters. As a rule, a cluster consists of several sectors.
For hard disks, the cluster size is determined during formatting and depends on the operating system version and disk size. But disk space is used inefficiently. For example, you need to save a file of 500 bytes. Knowing that each file can occupy space on an integer number of clusters, then in this case one cluster will be occupied. The file will be written with wasted disk space.
Quality characteristics of the hard drive
Sector search time. Sector search time (latency time) is the average time required for the desired sector to be under the head after it is brought to the track. The average seek time is equal to half of the disk rotation period and is calculated by the formula:
Average Search Time = 1/(Engine RPM*2)
That is, at a speed of 7200 rpm. the search time is 4.17 ms.
Reading speed and specification. The average data reading speed is about 40-45 MB / s.
It is believed that the controller on the motherboard specification UDMA / 33 is required to provide a data read speed of at least 33 MB / s. And modern specifications, for example, UDMA / 100 and UDMA / 133 must guarantee at least 100 and 133 MB / s.
The data transfer rate determines the amount of data that can be transferred from the drive to the computer and back in a certain amount of time. Data transfer speed is determined by two factors:
- The method of connecting drives, that is, the performance of the interface.
- The speed of reading data by the heads.
Reading speed(it is called the internal data exchange rate and is measured in MB / s) can be determined by the formula:
Reading speed = number of sectors per track * 512* * disk rotation speed / 1000000.
Drive speed measured in rpm, 512 is the number of bytes of data in the sector.
Average search time. Average seek time is the average time it takes heads to move from one cylinder to another. This indicator depends on the design of the actuator and is up to 10 ms.
Average access time. It is defined as the sum of the average search time and delay time and characterizes the average statistical time required to gain access to data recorded on an arbitrary sector.
Disc rotation speed. An indicator that is directly related to the speed of access and the speed of reading data. There are parameters 5400 rpm, 7200 rpm. (IDE); 10000 rpm, 15000 rpm (SCSI).
Hard drives are connected to the motherboard using special cables.
File Allocation Table
File Allocation Table- this is the area on the disk where the numbers of the clusters that deal with the files are entered. This does not include clusters that contain service information (boot sectors, the file allocation table itself, and root directory data). Microsoft's operating systems use the FAT (File Location Table) file system. A separate file system can be created on each logical drive. Thus, several types of file systems can exist on the same hard disk.
Popular file systems
FAT. This file system is used in MS DOS, Windows 3.x/9.x/2000, ME, XP, OS/2 operating systems.
HPFS. The name of this file system comes from High Performance File System, which means a highly productive file system. Supported by operating systems OS/2, Windows NT.
NTFS. The name of this file system comes from the Windows NT File System, which means the Windows NT / 2000 file system, supported by Windows NT / 2000, XP operating systems.
Logical drives
It is known that the computer assigns to all disks, regardless of their design, the logical names A:, B:, C:. The names A:, B: are assigned by default to floppy drives. The system logical drive, the one on which the operating system is recorded, is given the name C:.
Hard disk space can be divided into sections and logical drives. Operating systems work with logical drives, not physical ones.
Advantages of developing hard drives for several logical drives:
- Reduced wasted disk space.
- Simplified data structuring.
- The process of disk defragmentation, virus scanning, etc. is simplified.
On one disk, you can save working programs, on the other - documentation and archives, games (installation files). In the event of a malfunction, the loss of information is minimized.