Hardware FAQ 3 - RAM
Every day, a huge number of people on the forums ask a lot of questions, ask for help or recommend a product in one section or another. And our native goodgame() - not an exception. In today's creative, I will try to cover a wide range of the most popular and frequently asked hardware issues and their successive solutions. And today we will talk about RAM ...
What is Random Access Memory (RAM)?
A volatile part of a computer's memory system that temporarily stores data and instructions that the processor needs to perform an operation. A prerequisite is the addressability (each machine word has an individual address) of the memory. The transfer of data to/from RAM by the processor is performed directly, or through ultra-fast memory. The amount of RAM (by the way, it is also called RAM - random access memory) determines the number of tasks that a computer can simultaneously perform.
How does RAM work?
The principle of operation of RAM can be represented as follows. Since the cells are organized in a two-dimensional matrix, to access a particular cell, you must specify the address of the corresponding row and column. The RAS# (Row Access Strobe) and CAS# (Column Acess Strobe) pulses are used to select the address, at which the signal level (more precisely, the voltage) changes from high to low. These pulses are synchronized with the clock pulse, which is why random access memory (SDRAM) is also called synchronous. First, the activation signal of the required line is given, after which the RAS # pulse, and then CAS #. During a write operation, the same thing happens, except that in this case a special write enable pulse WE # (Write Enable) is applied, which should also change from high to low. After all the cells in the active row are completed, the Precharge command is executed, allowing you to move to the next row. There are other signals, but in the context of this article, they can be omitted so as not to unnecessarily complicate the material.
Scheme of interaction of RAM with other PC components:
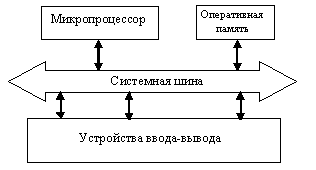
How is RAM divided?
1) Dynamic - English. DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory)
2) Static - SRAM (Static Random Access Memory)
1. Economical type of memory. To store a discharge (bit or trit), a circuit is used, consisting of one capacitor and one transistor (in some variations there are two capacitors). This type of memory solves, firstly, the problem of high cost (one capacitor and one transistor is cheaper than several transistors) and, secondly, compactness (where one trigger, that is, one bit, is placed in SRAM, eight capacitors and transistors can fit). There are also disadvantages. First, capacitor-based memory is slower, because if in SRAM a change in the voltage at the trigger input immediately leads to a change in its state, then in order to set one bit (one bit) of capacitor-based memory to one, this capacitor must be charged , and in order to set the discharge to zero, respectively, to discharge. And these are much longer operations (10 or more times) than switching the trigger, even if the capacitor is very small. The second significant minus is that capacitors are prone to charge “draining”; Simply put, capacitors discharge over time. Moreover, they are discharged the faster, the smaller their capacity. Due to the fact that the discharges in it are not stored statically, but “flow” dynamically in time, memory on capacitors got its name dynamic memory. In connection with this circumstance, in order not to lose the contents of the memory, the charge of the capacitors for recovery must be “regenerated” after a certain time interval. Regeneration is performed by the central microprocessor or memory controller, for a certain number of reading cycles when addressing by rows. Since all memory operations are periodically suspended to regenerate memory, this significantly reduces the performance of this type of RAM.
2. RAM that does not need to be regenerated (and is usually circuit-based on flip-flops) is called static random access memory or simply static memory. The advantage of this type of memory is speed. Since the flip-flops are assembled on gates, and the gate delay time is very small, the switching of the trigger state is very fast. This type of memory is not without drawbacks. First, the group of transistors that make up the flip-flop is more expensive, even if they are etched by the millions on a single silicon substrate. In addition, the group of transistors takes up much more space, since communication lines must be etched between the transistors that form the flip-flop. Used to organize ultra-fast RAM, critical to the speed of work.
How to choose RAM?
Pay attention when choosing:
1) Type of memory
2) Memory capacity
3) Memory clock
4) Latency (timings)
5) Manufacturer
6) Budget (price)
What is latency (timings)?
Latency (timings) - Time delays of the signal. Timing values usually look like, for example, 3-3-3-9 or 4-4-4-12 etc... In order, these are CAS Latency (CL), RAS to CAS Delay (tRCD), RAS Precharge Time (tRP ) and Active to Precharge (tRas), I won't go into details about what all this is, the main thing here is to know that the lower the timings, the better (when choosing from two modules of the same type, for example, PC2-6400).
From the user's point of view, information about timings allows you to roughly evaluate the performance of RAM before buying it. The memory timings of the DDR generation were given great importance, since the processor cache was relatively small and programs often accessed the memory. Much less attention is paid to DDR3 generation memory timings, since modern processors (for example, Intel Core DUO and Intel I5, I7) have relatively large L2 caches and are equipped with (again relatively) huge L3 cache, which allows these processors to access memory much less often, and in some cases, the entire program is placed in the processor cache
But what about the clock frequency?
As a rule, the computer runs faster if the clock speed of the RAM is higher. If you need DDR-2 memory, DDR2-800 with an effective frequency of 800 MHz or DDR2-1066 (1066 MHz) will do. If you need DDR-3 memory, then it is optimal to choose DDR3-1333, DDR3-1660 (1333/1600 MHz, respectively). Before buying, be sure to check which memory frequencies your motherboard supports.
What kind of cooling is used to cool the RAM?
1) Active (fans)
2) Passive (passives, radiators)
3) Water
5) Extreme (nitrogen, freon, liquid helium...)
6) Combined - for example, a passive radiator on which fans are mounted
What are the most popular manufacturers of RAM?
Kingston, OCZ, Corsair, Mushkin, Crucial, Geil, Team, Patriot, A-Data and many more)
What is the most popular amount of memory at the moment?
So to speak:
1) minimum -> 512-1024MB (512MB and 1GB)
2) average -> 2048-3072MB (2GB and 3GB)
3) optimal, recommended, for the future (with a deposit) -> 4096-6144MB (4GB and 6GB)
4) extreme -> from above 8096MB (8GB), i.e. 16GB, 24GB, 48GB and so on..
What is Dual Channel RAM?
Dual-channel mode - a mode of operation of computer random access memory (RAM), in which work with every second memory module is carried out in parallel with work with every first (that is, 1 (and 3) module(s) work in parallel with 2 (and 4), with each pair on its own channel, while on a single-channel memory controller all modules are serviced simultaneously by one controller (to put it simply, a channel).The total amount of available memory in dual-channel mode (as in single-channel mode) is equal to the total amount of installed memory modules.
Dual channel mode is supported when both DIMM channels have the same amount of memory installed. The technology and speed of devices on different channels may differ from each other, but the total amount of memory for each channel should be the same. Using different speed DIMMs on different channels will cause the memory to operate at the slower speed supported by all modules.
Example:

What are the rules for enabling dual channel mode?
Dual channel mode can be obtained by using an even number of DIMMs.
To enable dual-channel mode, the following conditions must be met:
Same density (128MB, 256MB, 512MB, etc.)
Memory channels A and B must be identical
Those. in dual-channel mode, memory of the same size, one frequency, one manufacturer, one type will work.
What determines the performance gain from the dual-channel memory mode?
type of memory;
Timings, memory delays;
Chipset type mat. board or type of memory controller;
Memory frequencies
And a number of other factors
What is Tri-Channel RAM?
Three-channel mode - a mode of operation of the computer's random access memory (RAM), in which three channels of memory operate in parallel. That is, 3 (or three pairs) of modules work in parallel - 1 (and 2), 3 (and 4) and 5 (and 6). Theoretically gives up to 300% performance compared to single-channel mode. In practice, it turns out to be not much more productive, and sometimes slower than the 2-channel mode.
Example:
What are the rules for enabling the three-channel mode in RAM?
Tri-channel mode can be obtained using three, six, or sometimes 9 memory modules.
To enable the three-channel mode, the following conditions must be met:
Same DIMM configuration per channel
Same density (128Mbps, 256Mbps, etc.)
Memory channels A, B and C must be identical
On most motherboards (with rare exceptions) symmetrical memory slots (slot 0 or slot 1) must be populated
What RAM modules are supported by today's motherboards?
1) DDR2 standard
2) DDR3 standard
3) the future of DDR4
Previously, there was "in" support for DDR memory (DDR1)
What is quad-channel memory mode?
In this mode, all RAM is divided into four blocks, each block of memory has a separate independent controller, due to which the effective bandwidth is quadrupled. To work in quad-channel mode, you must use memory modules of the same size with the same characteristics, installed in groups of four. Quad-channel memory controllers are primarily used in server platforms where high memory performance is required.
Example:

What is memory bandwidth?
Memory bandwidth (shortly: bandwidth) - the amount of data that can theoretically be transferred to / from memory in 1 second.
Calculated according to the formula:
PSP = amount of data transferred per clock * memory clock
Is there a noticeable difference between DDR3-1333MHz and DDR3-1600MHz, and will it give me a significant advantage?
Let's say right away! The difference between 1333 and 1600MHz is almost zero! (on the strength of 1-2%). It will not give additional performance! Save a lot of money for that. The difference is especially noticeable during overclocking (where each megahertz is worth its weight in gold) and volumetric rendering of heavy tasks (3dstudiomax, may, rendering, pyfast, etc.), There will be no difference in games!
But video cards also use DDR3/DDR4 memory, right? Is not it?
No, not really! Since modern graph. adapters use memory types: GDDR, GDDR2, GDDR3, GDDR4, GDDR5. Where the G prefix stands for graphics/gpu (graphics). In addition, the memory bandwidth of the graph is ten times higher.
What is the division of DRAM modules in a computer?
DIPP, DILL, SIPP
SIMM - (72pin, 30pin) - (One Inline Memory Module)
DIMM - 3.3V and 5V - (Dual Embedded Memory Modules) is actually two integrated memory modules on one board. Occupies the entire width of the tire.
SDR - (Single Data Rate), also called SDRAM (synchronous dynamic random access memory), an old type of DIMM memory (3.3 or 5 V), 168 pins, capacity from 16 MB to 512 MB, speed from 66 MHz to 133 MHz
DDR - (Double Data Rate) memory of a new type SDR, 3.3 V, 184pinů (different slots in place, not just one of the two), capacity from 64 to 2048 megabytes The difference is that it transmits data at the front edge (in beginning) and end of the clock pulse.
DDR2 - a new type of memory DDR, like DDR, have a higher frequency, they are becoming a real standard. Drawback: DDR2 latencies are higher than DDR.
DDR3 - They are slightly more expensive but more powerful. The maximum frequency is 3068MHz.
DDR4 - not yet available on the PC market, has been announced by JEDEC. Development and sales are expected in 2013 + DDR3 market shift is expected in 2015 (DDR4 will become the standard and DDR3 will gradually become a thing of the past). The maximum clock is 4266MHz at 1.05 V. Samsung already has the first prototypes of DDR4 memory
SO-DIMM - DIMM notebook memory, 72pin or 144/200-pin
RIMM - Rambus DRAM. Unlike DDR DIMM, it has only 16-bit bus width transfer, but it is much faster
How is RAM tested?
It is tested with several tests:
Memtest86+ - RAM test
This utility can be run from a boot floppy or CD. MemTest86+, in addition to its direct duties, determines the main characteristics of the computer, such as the chipset, processor and memory speed. The program has two modes of operation: basic and advanced (basic and advanced). They differ in testing time. In basic mode, you can determine some global memory problems, and in advanced mode, more thorough testing is carried out.
You can rewrite the program as a bootable floppy disk image or CD. Unzip the overwritten file and create a bootable disk by running the install command (for a floppy disk image) or burn the ISO file to a CD using a burning program such as Nero or Easy CD Creator.
Restart your computer and boot from the boot floppy or CD you received. Run MemTest86+. The main test will start automatically.
Docmem - RAM test
Docmem is a handy memory testing program that is well-deservedly popular. It can be rewritten from the manufacturer's website for free, you just need to register.
Windows memory diagnostic - RAM test
Microsoft offers its own diagnostic program, similar to the previous two. It comes as a standard installation file with a bootable CD image and a program to create a bootable floppy disk.
Windows memory diagnostic is a simpler program than the previous ones. In addition, it has an additional set of tests to test your computer. It allows you to determine which module is the source of the problem if there are several memory modules installed in the system.
What is overclocking? What does overclocking potential depend on?
Overclocking or overclocking (from the English overclocking) is an increase in the performance of computer components by operating them in forced (abnormal) modes of operation.
Well, to put it simply, overclocking is the forced operation of equipment at higher frequencies.
What is RAM overclocking?
Overclocking is easy: RAM!!!
Everything is well described and shown here :). We read, we disperse.Soooo! Well, that’s all for today, dear users and readers, I hope that this material was at least somehow useful. Next time consider the motherboard (MoBo). Good luck:)