A camera in a smartphone with large pixels or Ultrapixel technology (ultrapixel). How it works: UltraPixel Light-sensitive elements in conventional cameras
Users wondered what the new smartphone camera would be and whether the so-called “ultra pixels” would justify themselves. So far, the matter has not yet reached real shots and tests by independent reviewers, but the first official details about the HTC UltraPixel Camera appeared on the manufacturer's website.
With the new flagship, the Taiwanese company has decided to abandon the megapixel race. According to her firm conviction, other factors have a much greater influence on the quality of the picture and resolution, although important, still photos with a lower resolution, but taken with better optics and a sensor, will visually look better compared to “blurred multi-megapixel frames” .
Overall, HTC ImageSense technology includes: the UltraPixel Sensor, which has larger pixels and captures 300% more light than typical 13MP cameras; HTC ImageChip, which provides continuous autofocus, noise reduction, wider HDR range; high-quality optics with a maximum aperture of f / 2 (the fastest optics among smartphones, it allows you to capture 44% more light compared to the optics of the iPhone 5); Optical Image Stabilization, which allows you to significantly reduce the blurring of photos and videos.

HTC claims that pictures taken with its 4MP camera can be printed on 8" x 10" media. At the same time, users will definitely be satisfied with the quality of the print, which will surpass the pictures from the "multi-megapixel" cameras. You can see a comparison of pixel sizes in the figure below.


The UltraPixel camera allows you to capture the highest resolution image in as little as 1/48th of a second. For the closest competitors, including HTC One X, this figure is up to 1/30 of a second. The Dual Axis Optical Image Stabilization system delivers handheld blur-free images at shutter speeds down to 1/7.5s (internal tests).

Here are some sample shots offered by HTC. Unfortunately, these are not full size shots. So we'll have to wait for the first real tests.

Finally, we present more detailed specifications devices:
- Sensor: BSI CMOS;
- Sensor size: 1/3 inch;
- Pixel size: 2 x 2 mm;
- Maximum image resolution: 2688 x 1520 pixels;
- Video shooting: Full HD 1080p at up to 30 fps, HD 720p up to 60 fps, 1080p with HDR up to 28 fps, 768 x 432 pixels at up to 96 fps;
- Maximum aperture: f/2.0;
- Number of elements in the lens: 5;
- Continuous photography - up to 8 fps.
In 2013, the HTC One smartphone was released. In addition to other advantages, the device was equipped with a non-standard camera, which used a technology called Ultrapixel. The Taiwanese manufacturer called the introduction of ultrapixels a breakthrough in the field mobile photo, because, thanks to this event, other manufacturers will finally stop measuring the quality of cameras in smartphones using the number of megapixels.
Photosensitive elements in conventional cameras
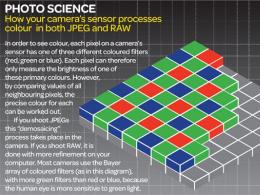
To begin with, let's go through a brief acquaintance with the principle of the arrangement of light filters on the matrix according to the Bayer scheme, which is used in almost all mobile photographic modules. The matrix contains elements that are sensitive to light. They are called "sensels". These elements capture light and transform it into electric charge. Each sensel can perceive one color - blue, green or red.
The disadvantage of the Bayer array of color filters is the appearance of color artifacts and moirés in the photo. To remedy the situation, a special anti-aliasing filter is used, which makes the images appear slightly blurry (hence the name "soap box"). This is clearly seen when rescaling pictures taken with amateur cameras and mobile photomodules.

In fact, most smartphone manufacturers try to put as many pixels on the sensor as possible in order to increase the original resolution of the resulting photo. As the number of megapixels increases, the area of each pixel decreases. As a result, they become less receptive to light, the photos turn out darker, and noise appears on them. To compensate for the lack of received illumination, the aperture is opened wider, and to combat noise, the merging of neighboring pixels is used.
The essence of UltraPixel technology and its benefits
HTC approached the issue of improving the camera from the other side: they reduced the resolution to 4 megapixels, but turned the pixels into ultrapixels, increasing their size to 2 micrometers, against 1.1 micrometers (microns) in 13 megapixel sensors.
![]()
UltraPixel technology provides for the placement of sensors on the photomatrix in three layers, each of which separately perceives red, blue and green colors. At the same time, the area of photosensitive elements is 3 times larger (up to 4 µm square) in relation to "ordinary" sensels.

A similar principle has long been used in the Foveon matrices that Sigma DSLRs come with.

In fact, this solution has several advantages at once:
- ultrapixels perceive about 300% more light, respectively, you can get better photos in the dark;
- a significant reduction in the amount of noise when shooting in low light conditions;
- moving people and objects in the resulting photo are practically not smeared;
- thanks to a wider HDR range, dark areas are highlighted, and light areas, on the contrary, are not overexposed;
- there is no need for an anti-aliasing filter, which is the cause of blurring in the Bayer matrix.
Disadvantages of UltraPixel Technology
Theoretically, this idea has solid advantages. but major mistake there was a decision to stop at 4 megapixels. Because of this, when shooting distant objects and landscapes, photos suffer from poor detail.
But why only 4 megapixels, couldn't it be more? Of course you can. However, it should be borne in mind that ultra-pixels will require much more space than "ordinary" ones. Accordingly, the physical size of the photomatrix will "grow" in size, and with it the module itself. The mass consumer is accustomed to a small, compact camera eye in smartphones, so not everyone will perceive a sharp change in its diameter. Therefore, in HC, introducing UltraPixel, they decided to limit themselves to a lower resolution in favor of the design of the mobile device case.
Perhaps in the future, camera phones will be equipped with a much larger matrix than today, where ultrapixels will be used instead of "ordinary" pixels.
Where else are ultrapixels used?
The word "UltraPixel" was invented by HTC marketers, who first tested the technology of increasing pixels on the camera's photomatrix in a smartphone. The idea turned out to be promising, and later found application in Apple devices (iPad Air 2), as well as Google, which together with LG and Huawei released the Nexus 5X and Nexus 6P. The name UltraPixel never caught on, so it is not used in descriptions of the characteristics of these devices.
Later, Samsung showed at the exhibition new smartphone- Galaxy S7 edge, with a 1/2.5” matrix size and enlarged pixels up to 1.4 microns. For reference: in the Galaxy S6, the size of the 16-megapixel photomatrix is 1/2.6″, and each pixel is 1.2 microns.
Looking at these sample photos taken with the Note 5 (left) and the Galaxy S7 (right), both shots seem to be about the same quality.


However, with a 100% increase in individual fragments, a significant difference in detail is immediately visible.

Enlarged pixels are used in professional-level photographic equipment, that is, in DSLRs. Thanks to this, even the most affordable SLR cameras with a standard (complete) lens are significantly ahead of rather steep soap dishes when shooting in low light conditions. They capture more light, and the finished shots tend to have less noise. If the pixel density in DSLRs were the same as in conventional compact cameras, as well as smartphones, the resolution would exceed 120 megapixels. Meanwhile, the most sophisticated models on this moment can shoot with a resolution of 36, maximum 51.4 megapixels.
The difference between shooting in low light cameras with large pixels and ordinary
You will also like:

HTC has announced its long-awaited flagship HTC 10, which is the epitome of an obsession that the company has been working on for a whole year. The HTC One concept has been revealed in a whole new light. So, dual stereo speakers disappeared from the front panel, as well as a strip, which for many was still an irritant. Instead, it uses rounded 2.5D glass, a Home button with a built-in fingerprint scanner, and two touch keys. The case is made of metal, but a special beveled panel is used. The thickness at the extreme point reaches 3 mm. The main feature, of course, is the cameras. It uses 12-megapixel and 5-megapixel f / 1.8 modules with optical image stabilization (in both cases). The main camera is made using Ultrapixel 2 technology. This is a wide-angle (80 degrees) BSI sensor with a pixel size of 1.55 microns. There is laser autofocus and dual LED flash. The front camera also has a wide viewing angle (86 degrees), can record video in 4K format and has a set of effects for selfies.
The next thing the company was obsessed with on the HTC 10 was sound. The Taiwanese have equipped the flagship with a 24-bit DAC with Hi-Res Audio support. In addition, the BoomSound Hi-Fi Edition technology is implemented, which separates high-frequency and woofers, each of which has its own amplifier. This is what makes it possible to achieve rich sound without the traditional speaker layout of the HTC One line. Hardware potential, according to HTC, will help reveal the new headphones that will be bundled with the HTC 10 in some regions. The accessory is certified by Hi-Res Audio, has membranes made of 8µm thick polymer, which is used in the aerospace industry.

And now about performance. Following the example of LG, HTC 10 will be released in two versions. Depending on the region, the device will be available in Snapdragon 820 (quad-core Kryo) and Snapdragon 652 (qualcomm octa-core) versions. The latter has a Lifestyle prefix and it will be available in Russia in this form. 3 or 4 GB are also responsible for speed random access memory and Android 6.0.1 Marshmallow with Sense UI 8.0 shell with Boost + technology (an acceleration system that dynamically manages smartphone resources, which allows you to influence energy costs for work background programs. By the way, in both cases the device received non-removable battery 3000 mAh with technology fast charging Qualcomm Quick Charge 3.0. According to the manufacturer, it will provide offline work HTC 10 with 5.2” LCD5 display (resolution 2560 x 1440 pixels) for two days.

The HTC 10 is now available for pre-order in the US. There it was priced at $700 (unlocked version with 4 GB RAM and 32 GB ROM), and the color palette includes black and silver. The release of the HTC 10 Lifestyle in Russia will be announced later.


Specifications HTC 10 / HTC 10 Lifestyle:
- Network: GSM/GPRS/EDGE (850/900/1800/1900MHz), UMTS/HSDPA (850/900/1900/2100MHz), LTE (800/900/1800/2600MHz)
- Platform (at time of announcement): Android 6.0.1 Marshmallow with Sense 8.0
- Display: 5.2", 2560 x 1440 pixels, Super LCD5, 564 ppi, Gorilla glass Glass 4
- Camera: 12MP, Ultrapixel 2, BSI, 1.55µm, f/1.8, laser autofocus, optical image stabilization, dual LED flash, 4K@30fps video recording
- Front camera: 5MP, 1.34µm, f/1.8, optical image stabilization, 1080p video recording
- Processor: 4 cores, Kryo, up to 2.2 GHz, Qualcomm Snapdragon 820 | 8 cores, 64 bits, up to 1.8 GHz, Snapdragon 652 (Lifestyle)
- Graphics chip: Adreno 530
- RAM: 4 GB (3 GB for Lifestyle)
- Internal memory: 32/64 GB
- Memory card: microSD (up to 2 TB)
- GPS and GLONASS
- Bluetooth 4.2 with aptX
- WiFi (802.11a/b/g/n/ac)
- USB Type-C
- HDMI MHL 3.0
- nano SIM
- 24-bit DAC, BoomSound Hi-Fi Edition with Dolby Audio
- Accelerometer, proximity sensor, ambient light sensor, gyroscope, barometer, fingerprint scanner
- Battery: non-removable, 3000 mAh, Quick Charge 3.0
- Dimensions: 145.9 x 71.9 x 3.0-9.0 mm
- Weight: 161g
"Ultrapixel
"The era of megapixels has come to an end"- summed up the head HTC Peter Chow(Peter Chou) during yesterday's announcement of a new flagship smartphone HTC One, which was equipped with a revolutionary camera with technology "Ultrapixel". The Taiwanese company reaffirmed the rule that a large number of pixels does not yet guarantee the quality of the picture. But what is the revolutionary nature of the transition from megapixels to "ultrapixels"?
![]()
Camera HTC UltraPixel differs not in the number of pixels, but in their size. Simply put, the pixels are slightly larger than the rest. mobile cameras (2 microns vs 1.1-1.4 microns). This allows the camera to capture 300 % more light compared to conventional sensors even in today's most advanced sensors 13 -megapixel cameras. As a result, the camera is able to take high-quality pictures in any light (even in low light).
![]()
Larger pixels capture more light
To keep blurring to a minimum, HTC uses a multi-axis optical image stabilization system in both the main and front cameras, so that photos are clearer. By the way, 2,1 -megapixel front-camera able to create video in resolution 1080p, and a new graphics chip guarantees continuous autofocus at up to 200ms.

The difference is obvious: HTC One (top), iPhone5 (bottom).
An example of shooting in HDR mode:
Before release HTC One only a short time left on sale and we look forward to comparing "ultrapixel" camera with Nokia 808 PureView or Nokia Lumia 920. In general, one can only welcome the desire of a Taiwanese company to innovative technologies and refusal "megapixel racing".
Features of the HTC UltraPixel camera:
- Sensor type: CMOS BSI
- Sensor size: 1/3 inch
- Pixel size: 2mm x 2mm
- Resolution: 2688 x 1520 with 16:9 aspect ratio = = 4MP
- Shutter speed up to 48fps with limited motion blur
- Video resolutions: 1080p up to 30fps, 720p up to 60fps, 1080p with HDR up to 28fps, 768x432 up to 96fps
- Focal length: 3.82mm
- Optical F/# aperture F/2.0
- Number of lenses: 5P
- Optical Image Stabilizer: 2-axis, +/- 1 degree (average), 2000 cycles per second
- Maximum fps: up to 8 fps continuous shooting
Back in kindergarten, we were taught to compare numbers, so we can easily say that 13 is more than 4. HTC M8 got a 4 megapixel camera, and HTC One mini 2 by 13 megapixels. Who will take better photos? And the one whose technology is cooler.
4 > 13
Despite the numerical difference in the number of pixels, the quality of the HTC M8 is noticeably higher than that of its mini version. Calmly! You didn't miss the math reform, and 13 is still more than 4. But when it comes to smartphone cameras, you need to look at all the details when comparing technology that looks the same at first glance.
With a visual comparison of the quality HTC cameras M8, HTC One mini 2 and HTC Desire 816, the superiority of the M8's 4-megapixel camera over its opponents can be seen with the naked eye. It offers more consistent and reliable performance across a wide range of lighting scenarios. The M8 camera delivers more natural colors, contrast and easy the best quality photos, while the 13-megapixel cameras look washed out, almost hazy and unnatural. This is one of the side effects in this direction of smartphone construction.
And the reason is very simple.
It's all about the size of the pixels themselves. HTC One mini 2 does not use HTC's "ultra pixel technology", but is equipped with a conventional sensor, only with a higher resolution. One M8 received the same sensor, but with a lower resolution, but with a larger pixel size - 2 microns, as opposed to 1.1 microns in a 13-megapixel camera.
The difference is visible primarily in the issue of illumination. The M8 captures more light, which means more “data”, which provides better photo quality than the One mini 2 and Desire 816. Therefore, in low light conditions, the One M8 will not let you down. The only thing the M8 is inferior to its counterparts is in the final photo resolution, which will be three times smaller. However, to share photos in in social networks, where high resolution is simply not required, and often photos are compressed on the contrary, the M8 camera will be enough.