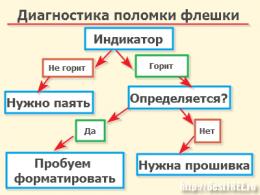
Collection and processing of information. Information processing technology
The technological process of data processing in information systems is carried out using:
technical means of collecting and recording data;
means of telecommunications;
storage, retrieval and data retrieval systems;
funds computational processing data;
technical means of office equipment.
In modern information systems, technical means of data processing are used in a complex manner, on the basis of a technical and economic calculation of the feasibility of their use, taking into account the price / quality ratio and the reliability of the technical means.
Information Technology
Information technology can be defined as a set of methods– techniques and algorithms for data processing and tools– software and technical means of data processing.
Information technology can be roughly divided into categories:
Basic information technologies are universal technological operations of data processing, which, as a rule, do not depend on the content of the information being processed, for example, launching programs for execution, copying, deleting, moving and searching for files, etc. They are based on the use of widely used software and hardware for data processing.
Special information technologies - a complex of information-related basic information technologies, designed to perform special operations, taking into account the content and / or form of data presentation.
Information technologies are a necessary basis for the creation of information systems.
Information Systems
An information system (IS) is a communication system for collecting, transferring, processing information about an object, supplying employees of various ranks with information to implement the management function.
IS users are organizational units of management - structural units, management personnel, performers. The content basis of IS is functional components - models, methods and algorithms for the formation of control information. The functional structure of IS is a set of functional components: subsystems, task complexes, information processing procedures that determine the sequence and conditions for their implementation.
The introduction of information systems is carried out in order to increase the efficiency of the production and economic activities of the facility through not only processing and storing routine information, automating office work, but also through fundamentally new management methods. These methods are based on modeling the actions of the organization's specialists when making decisions (artificial intelligence methods, expert systems, etc.), using modern means of telecommunications (e-mail, teleconferences), global and local computer networks etc.
Classification of IP is carried out according to the following criteria:
nature of information processing;
scale and integration of IS components;
information technology architecture of IS.
According to the nature of information processing and the complexity of IP processing algorithms, it is customary to divide into two large classes:
IS for operational data processing. These are traditional ISs for accounting and processing large volume primary data using strictly regulated algorithms, a fixed database structure (DB), etc.
Support and decision-making IS. They are focused on the analytical processing of large amounts of information, the integration of heterogeneous data sources, the use of methods and tools for analytical processing.
Currently, the main information technology architectures have developed:
IS with centralized data processing,
file server architecture
client-server architecture.
Central processing involves the integration of the user interface, applications and database on one computer PS.
IN architecture “file server” many network users are provided files host computer on the network, called file server. These can be individual user files, database files, and application programs. All data processing is carried out on users' computers. Such a computer is called workstation(RS). It installs the PS of the user interface and applications that can be entered both from the PC input devices and transmitted over the network from the file server. The file server can also be used for centralized storage of individual users' files that they send over the network from the PC. Architecture file server” is mainly used in local computer networks.
IN architecture “client-server“The software is focused not only on the collective use of resources, but also on their processing at the location of the resource at the request of users. Client-server architecture software systems consist of two parts: software server and user-client software. The operation of these systems is organized as follows: client programs run on the user's computer and send requests to the server program that runs on the shared computer. The main data processing is performed by a powerful server, and only the results of the query are sent to the user's computer. So, for example, a database server is used in powerful DBMS such as Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle and others working with distributed databases. Database servers are designed to work with large amounts of data (tens of gigabytes or more) and a large number of users, while providing high performance, reliability and security. The "client-server" architecture, in a certain sense, is the main one in the applications of global computer networks.
System unit consists of a case with a power supply and a motherboard (system) board. Power supply converts alternating current in D.C. low voltage. The power of the power supply determines how many additional devices that do not have their own power supply can be connected to the system unit.
Motherboard - the main part of the computer, with the help of which other elements are combined. This is a big printed circuit board, which houses the system and local buses, microprocessor, RAM, additional chips and slots for connecting additional devices. motherboards unified by standard sizes (at present, AT, ATX, LPX, NLX are the most common).
System bus designed to transfer information between the central processing unit and other computer components. Modern computers use EISA, PCI, PCMCIA, AGP buses. Buses are divided into synchronous, where data is transmitted according to the clock frequency (RSI), and asynchronous, where data is transmitted at random times (EISA).
CPU (Central Processing Unit - CPU) is a large integrated circuit implemented on a single semiconductor chip, which is designed for software-controlled information processing. Depending on the type of instructions that are executed, there are CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computer) and RISC (Reduce Instruction Set Computer) microprocessors. The first microprocessors were CISC processors. RISC processors use instructions of the same length, which are simpler and faster to execute.
The bit depth of the microprocessor determines how many bits of information are processed in it in one clock cycle. The first microprocessor Intel 4004, which appeared in 1971 p. clock frequency 750 kHz. With the development of processors, their clock frequency, bit depth of registers and external data bus increase, and command decoding improves. Modern computers Pentium IIIs are clocked at 450 MHz or higher.
RAM may be dynamic or static. RAM dynamic type is a random-selection memory (Dynamic Random Access Memory, DRAM). Each bit of such memory is represented as the presence or absence of a charge on a capacitor formed in the structure of a semiconductor crystal. Static memory (Static RAM - SRAM) as a unit cell uses a static trigger, consisting of several transistors. This memory has high performance, but it is more expensive.
According to the method of accessing data, memory is divided into synchronous and asynchronous. Dynamic memory chips are made in different packages: SIMM (Single In line Memory Module), DIMM (Dual In line Memory Module). SDRAM is synchronized with a system timer that controls the CPU. SDRAM II (DDR - Double Data Rate) uses more precise internal timing, which doubles the access speed.
The video memory uses dynamic random access memory, which has a number of features: access is carried out in fairly large blocks, data is rewritten without interrupting the reading procedure.
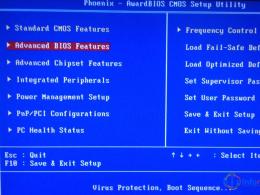
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) - a special chip that contains a set of input-output programs, with the help of which operating system And application programs can interact with computer devices on physical level; a program for testing a computer and its devices, which starts when the computer is turned on; setup program to change the settings that define the configuration of the computer.
Information storage devices
Information storage devices are intended for long-term storage large amounts of information. This type of memory, unlike operational memory, is energy-independent, i.e. information is not lost when the computer's power is turned off. The operation of information storage devices is based on different principles (magnetic, optical, etc.). The cost of storing a unit of information on them is much lower compared to RAM, and the volume of media used in these devices is much larger, but the time to access information in them is even longer. Distinguish between removable and non-removable media drives. The reliability of storing information on non-removable media is much greater, and the access time is less.
To integrate storage media into a computer, special interfaces have been developed, of which the most popular today are IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) and SCSI (Small Computer System Interface).
The SCSI interface was developed in 1970 p. Up to eight devices can be connected to the bus, including the main SCSI controller. The SCSI controller has its own BIOS that manages the 8-bit SCSI bus, freeing up the CPU.
The IDE interface was proposed in 1988. The controller functions are implemented in the electronic part of the device. Data exchange can be carried out both through the central processor (RIO - Programmed Input / Output), and directly (DMA - Direct Memory Access).
streamers - magnetic tape drives. They are usually used to create large archive copies and have built-in data compression.
Hard disk drives - These are devices with an invariable wear. they are often referred to as Winchesters. They contain a mechanical drive, read-write heads for several media, and a controller that ensures the operation of the device and data transfer. To record information, the magnetic properties of the surface of the media discs are used.
Hard disk drives differ from each other primarily in their capacity and speed. The speed of a disk is characterized by two indicators: the time it takes to access data on the disk and the speed of reading and writing data to the disk.
When reading or writing short blocks of data located in different parts of the disk, the speed of work is determined by the data access time, and when reading or writing large blocks of data, it is much more important throughput path of exchange with the disk.
Removable drives: drives for floppy disks in size "and 5.25" - FDD (Floppy Disk Drive), magneto-optical disks - MOD (Magneto-Optical Disk), CD-ROM, CD-RW, DVD (Digital Versatile Disk). They allow you to transfer information from one computer to another and make archival copies of the information contained on your hard drive.
It should be noted that the access time and read-for-write speed depend not only on the device itself, but also on the parameters of the entire path of exchange with the disk: on the speed of the disk controller, system bus, and CPU computer.
Keyboard is the main input device for the computer. This is a set of mechanical sensors that perceive keystrokes and close a certain electrical circuit. Many types of keyboards have been developed, differing mainly in ergonomic qualities. Additional devices, such as a microphone, can be built into the keyboard. The most common are two types of keyboards: with mechanical and membrane switches. The technology based on membrane switches is considered more advanced, although it does not have any special advantages.
Mice And trackballs - These are coordinate devices for entering information into a computer. They have two or three control buttons, but the third button is almost never used. In addition, a two-button mouse may have a special wheel for quickly viewing multi-page information. Both mechanical mice and optical mice are common, which allow you to achieve greater accuracy. There are three ways to connect a mouse: serial COM port, PS/2 port, and USB port. IN trackballs it is not the body that moves, but only its ball, which allows you to increase the accuracy of cursor control and does not require extra space for work. Trackballs are commonly used in laptop computers.
Scanner is a device with which information from paper media is entered into a computer. The optical resolution of the scanner determines the size of the elements that the scanner transmits without distortion. Resolution depends on the number of elements used per unit length in the ruler photosensitive elements and from the step of moving the scanning device. It is measured in dpi - the number of dots per inch.
All scanner models can be divided into manual, flatbed, roll and drum. Handheld scanners must be moved by hand over the material being scanned. In flatbed scanners, the scanning head moves across the image using a stepper motor. Roll scanners feed images through a scanning device. Drum scanners use a photoelectric multiplier as a photosensitive element.
In addition, scanners are divided into single pass, that they use three rulers to simultaneously obtain information about three primary colors, and triprochіdnі, that in one pass they receive information about one color. The color bit depth of a scanner is determined by the number of bits used to store color information. Modern scanners use at least 24 bits (8 bits per color).
To communicate with a computer, scanners use serial and parallel ports, as well as SCSI interfaces and USB.
electronic tablet - coordinate converter, used mainly for CAD tasks.
Joystick - analog lever device for input of coordinate information. It is used almost exclusively in games and simulators.
The complex of technical means of information processing is a set of autonomous devices for collecting, accumulating, transmitting, processing and presenting information, as well as office equipment, management, maintenance and other means. A number of requirements are imposed on the complex of technical means:
Ensuring problem solving with minimal cost required accuracy and reliability
Possibility of technical compatibility of devices, their aggregability
Ensuring high reliability
Minimum acquisition costs
Domestic and foreign industry produces a wide range of technical means of information processing, which differ element base, design, use of various storage media, operational characteristics, etc.
Classification of technical means of information processing
Technical means information processing are divided into two large groups. These are the main and auxiliary means of processing.
Auxiliaries are equipment that ensures the performance of fixed assets, as well as equipment that facilitates and makes managerial work more comfortable. Auxiliary means of information processing include office equipment and repair and preventive means. Office equipment is represented by a very wide range of tools, from office supplies, to delivery, reproduction, storage, search and destruction of basic data, administrative and production communication tools, and so on, which makes the work of a manager convenient and comfortable.
Fixed assets are the tools of labor for automated information processing. It is known that for the management of certain processes, certain management information is required that characterizes the states and parameters technological processes, quantitative, cost and labor indicators of production, supply, marketing, financial activities, etc. to fixed assets technical processing include: means of registration and collection of information, means of receiving and transmitting data, means of preparing data, input means, means of processing information and means of displaying information. Below, all these tools are discussed in detail.
Obtaining primary information and registration is one of the labor-intensive processes. Therefore, devices for mechanized and automated measurement, data collection and recording are widely used. The range of these funds is very extensive. These include: electronic balance, various counters, scoreboards, flow meters, cash registers, banknote counting machines, ATMs and much more. This also includes various production registrars designed to draw up and record information about business transactions on machine media.
Means of receiving and transmitting information. Information transfer refers to the process of sending data (messages) from one device to another. An interacting set of objects formed by data transmission and processing devices is called a network. Combine devices designed to transmit and receive information. They provide information exchange between the place of its origin and the place of its processing. The structure of means and methods of data transmission is determined by the location of information sources and data processing facilities, the volume and time for data transmission, types of communication lines and other factors. Data transmission means are presented subscriber points(AP), transmission equipment, modems, multiplexers.
Data preparation tools are represented by devices for preparing information on machine media, devices for transferring information from documents to media, including computer devices. These devices can sort and correct.
Input means are used to perceive data from computer media and enter information into computer systems.
Means of information processing play the most important role in the complex of technical means of information processing. Processing tools include computers, which in turn are divided into four classes: micro, small (mini); large and supercomputers. Microcomputers are of two types: universal and specialized.
Both universal and specialized can be both multi-user - powerful computers equipped with several terminals and operating in time-sharing mode (servers), and single-user (workstations) that specialize in performing one type of work.
Small computers- work in time-sharing and multi-tasking mode. Their positive side is reliability and ease of operation.
Mainframes- (main farms) are characterized by a large amount of memory, high fault tolerance and performance. It is also characterized by high reliability and data protection; the ability to connect a large number of users.
supercomputer- these are powerful multiprocessor computers with a speed of 40 billion operations per second.
Server - a computer dedicated to processing requests from all stations on the network and providing these stations with access to system resources and distributing these resources. The universal server is called - server-application. Powerful servers can be attributed to small and large computers. Now Marshall servers are the leader, and there are also Cray servers (64 processors).
Information display means are used to display calculation results, reference data and programs on machine media, printing, screen, and so on. Output devices include monitors, printers, and plotters.
A monitor is a device designed to display information entered by the user from the keyboard or output by a computer.
The printer is a device for outputting text and graphic information to paper.
The plotter is a device for outputting drawings and diagrams of large formats to paper.
The technological process of data processing in information systems is carried out using:
technical means of collecting and recording data;
means of telecommunications;
storage, retrieval and data retrieval systems;
means of computing data processing;
technical means of office equipment.
In modern information systems, technical means of data processing are used in a complex manner, on the basis of a technical and economic calculation of the feasibility of their use, taking into account the “price/quality” ratio and the reliability of the technical means.
Information Technology
Information technology can be defined as a set of methods– techniques and algorithms for data processing and tools– software and technical means of data processing.
Information technology can be roughly divided into categories:
Basic information technologies are universal technological operations of data processing, which, as a rule, do not depend on the content of the information being processed, for example, launching programs for execution, copying, deleting, moving and searching for files, etc. They are based on the use of widely used software and hardware for data processing.
Special information technologies - a set of information-related basic information technologies designed to perform special operations, taking into account the content and / or form of data presentation.
Information technologies are a necessary basis for the creation of information systems.
Information Systems
An information system (IS) is a communication system for collecting, transferring, processing information about an object, supplying employees of various ranks with information to implement the management function.
IS users are organizational units of management - structural units, management personnel, performers. The content basis of IS is functional components - models, methods and algorithms for the formation of control information. The functional structure of IS is a set of functional components: subsystems, task complexes, information processing procedures that determine the sequence and conditions for their implementation.
The introduction of information systems is carried out in order to increase the efficiency of the production and economic activities of the facility through not only processing and storing routine information, automating office work, but also through fundamentally new management methods. These methods are based on modeling the actions of the organization's specialists when making decisions (artificial intelligence methods, expert systems, etc.), using modern means of telecommunications (e-mail, teleconferences), global and local computer networks, etc.
Classification of IP is carried out according to the following criteria:
nature of information processing;
scale and integration of IS components;
information technology architecture of IS.
According to the nature of information processing and the complexity of IP processing algorithms, it is customary to divide into two large classes:
IS for operational data processing. These are traditional ISs for accounting and processing large volume primary data using strictly regulated algorithms, a fixed database structure (DB), etc.
Support and decision-making IS. They are focused on the analytical processing of large amounts of information, the integration of heterogeneous data sources, the use of methods and tools for analytical processing.
Currently, the main information technology architectures have developed:
IS with centralized data processing;
architecture of the “file-server” type;
client-server architecture.
Central processing involves the integration of the user interface, applications and database on one computer PS.
IN architecture “file server” many network users are provided files host computer on the network, called file server. These can be individual user files, database files, and application programs. All data processing is carried out on users' computers. Such a computer is called workstation(RS). It installs the PS of the user interface and applications that can be entered both from the PC input devices and transmitted over the network from the file server. The file server can also be used for centralized storage of individual users' files that they send over the network from the PC. Architecture file server” is mainly used in local computer networks.
IN architecture “client-server“The software is focused not only on the collective use of resources, but also on their processing at the location of the resource at the request of users. Client-server architecture software systems consist of two parts: server software and user-client software. The operation of these systems is organized as follows: client programs run on the user's computer and send requests to the server program that runs on the shared computer. The main data processing is performed by a powerful server, and only the results of the query are sent to the user's computer. So, for example, the database server is used in powerful DBMS, such as Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, etc. working with distributed databases. Database servers are designed to work with large amounts of data (tens of gigabytes or more) and for a large number of users, while providing high performance, reliability and security. The "client-server" architecture in a certain sense is the main one in the applications of global computer networks.
1.1 Data processing modes
When designing technological processes, they are guided by the modes of their implementation. The mode of implementation of the technology depends on the volume and time features of the tasks being solved: periodicity and urgency, requirements for the speed of message processing, as well as on the regime capabilities of technical means, and primarily computers. There are: batch mode; real time mode; time sharing mode; regulatory regime; request; dialog; teleprocessing; interactive; single program; multiprogram (multi-processing).
batch mode. When using this mode, the user does not have direct communication with the computer. Collection and registration of information, input and processing do not coincide in time. First, the user collects information, forming it into packages in accordance with the type of tasks or some other sign. (As a rule, these are tasks of a non-operational nature, with a long-term validity of the results of the solution). After the reception of information is completed, it is entered and processed, i.e., there is a processing delay. This mode is used, as a rule, with a centralized method of information processing.
Dialog mode (request) mode, in which there is a possibility for the user to directly interact with the computer system during the user's work. Data processing programs are permanently stored in the computer memory if the computer is available at any time, or during a certain period of time when the computer is available to the user. The interaction of a user with a computer system in the form of a dialogue can be multifaceted and determined by various factors: the language of communication, the active or passive role of the user; who is the initiator of the dialogue - the user or the computer; response time; dialogue structure, etc. If the dialogue is initiated by the user, then he must have knowledge of working with procedures, data formats, etc. If the initiator is a computer, then the machine itself tells at each step what to do with the various possibilities of choice. This method of operation is called “menu selection”. It provides support for user actions and prescribes their sequence. In this case, less training is required from the user.
The interactive mode requires a certain level of technical equipment of the user, i.e. the presence of a terminal or PC connected to the central computer system by communication channels. This mode is used to access information, computing or software resources. The ability to work in an interactive mode can be limited in terms of the start and end time of work, or it can be unlimited.
Sometimes a distinction is made between dialogue and interrogative modes, then the query is understood as a one-time access to the system, after which it issues a response and turns off, and the dialog is the mode in which the system issues a response after the request and waits for further user actions.
Real time mode. Means the ability of a computing system to interact with controlled or controlled processes at the pace of these processes. The reaction time of the computer must satisfy the pace of the controlled process or the requirements of users and have a minimum delay. As a rule, this mode is used in decentralized and distributed data processing.
The teleprocessing mode allows remote user interact with the computer system.
Interactive mode implies the possibility of two-way interaction between the user and the system, i.e. the user has the ability to influence the data processing process.
The time-sharing mode implies the ability of the system to allocate its resources to a group of users in turn. Computing system serves each user so quickly that it gives the impression of several users working at the same time. This possibility is achieved through the appropriate software.
Single-program and multi-program modes characterize the ability of the system to work simultaneously on one or more programs.
Scheduled mode is characterized by certainty in time of individual tasks of the user. For example, receiving results summaries at the end of the month, calculating payroll sheets for certain dates, etc. Terms of decision are set in advance according to the regulations, as opposed to arbitrary requests.
1.2 Data processing methods
The following methods of data processing are distinguished: centralized, decentralized, distributed and integrated.
Centralized presupposes existence. With this method, the user delivers the initial information to the CC and receives the results of processing in the form of effective documents. A feature of this processing method is the complexity and laboriousness of establishing a fast, uninterrupted connection, a large workload of CC information (since its volume is large), regulation of the timing of operations, organization of system security from possible unauthorized access.
decentralized processing. This method is associated with the emergence of PCs, which make it possible to automate a specific workplace.
The distributed method of data processing is based on the distribution of processing functions between different computers included in the network. This method can be implemented in two ways: the first involves the installation of a computer in each network node (or at each level of the system), while data processing is carried out by one or more computers, depending on the actual capabilities of the system and its needs at the current time. The second way is to place a large number of different processors inside one system. This way is used in banking and financial information processing systems, where a data processing network is needed (branches, departments, etc.). Advantages of the distributed method: the ability to process any amount of data within a given time frame; high degree of reliability, since in case of failure of one technical means it is possible to instantly replace it with another; reduction of time and costs for data transmission; increasing the flexibility of systems, simplifying the development and operation of software, etc. The distributed method is based on a complex of specialized processors, i.e. Each computer is designed to solve certain tasks, or tasks of its own level.
An integrated way of processing information. It provides for the creation information model managed object, that is, the creation distributed base data. This method provides maximum convenience for the user. On the one hand, databases provide for collective use and centralized management. On the other hand, the amount of information, the variety of tasks to be solved require the distribution of the database. Integrated information processing technology improves the quality, reliability and speed of processing. processing is carried out on the basis of a single information array, once entered into the computer. A feature of this method is the technological and time separation of the processing procedure from the procedures for collecting, preparing and entering data.