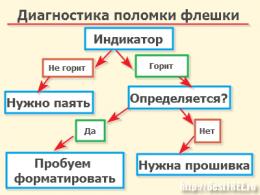
«Computer networks, network and telecommunication technologies. Internet
Computer network (CS) - a set of computers and terminals connected via communication channels in single system, which satisfies the requirements of distributed data processing .
In general, under telecommunications network (TS) understand a system consisting of objects that perform the functions of generating, transforming, storing and consuming a product, called points (nodes) of the network, and transmission lines (communications, communications, connections) that transfer the product between points.
Depending on the type of product - information, energy, mass - information, energy and material networks are distinguished, respectively.
Information network (IS) - a communication network in which the product of generating, processing, storing and using information is information. Traditionally for transmission sound information are used telephone networks, images - television, text - telegraph (teletype). Nowadays information is becoming more and more widespread. integrated service networks, allowing to transmit sound, image and data in a single communication channel.
Computing network (CN) - information network which includes computing equipment. The components of a computer network can be computers and peripherals, which are sources and receivers of data transmitted over the network.
Aircraft are classified according to a number of criteria.
- 1. Depending on the distance between network nodes, aircraft can be divided into three classes:
- · local(LAN, LAN - Local Area Network) - covering a limited area (usually within the remoteness of stations no more than a few tens or hundreds of meters from each other, less often 1 ... 2 km);
- · corporate (enterprise scale)- a set of interconnected LANs covering the territory where one enterprise or institution is located in one or several closely spaced buildings;
- · territorial- covering a significant geographical area; Among territorial networks, one can single out regional networks (MAN - Metropolitan Area Network) and global networks (WAN - Wide Area Network), having, respectively, regional or global scales.
Particularly distinguish the global network of the Internet.
2. An important feature of the classification of computer networks is their topology, which determines the geometric arrangement of the main resources of the computer network and the connections between them.
Depending on the topology of node connections, there are bus (backbone), ring, star, hierarchical, and arbitrary networks.
Among the LANs, the most common are:
- · bus- a local network in which communication between any two stations is established through one common path and the data transmitted by any station simultaneously become available to all other stations connected to the same data transmission medium;
- · ring- the nodes are connected by a ring data transmission line (only two lines go to each node). Data, passing through the ring, alternately becomes available to all network nodes;
- · stellar (star)- there is a central node from which data transmission lines diverge to each of the other nodes.
The topological structure of the network has a significant impact on its throughput, the network's resilience to failures of its equipment, the logical capabilities and cost of the network.
Mouse
Keyboard
Keyboard – keyboard control device for a personal computer. Serves for entering alphanumeric data, as well as control commands. The combination of monitor and keyboard provides the simplest user interface.
Keyboard functions do not need to be supported by special system programs (drivers). The software required to get started with the computer is already on the read-only memory (ROM) chip in the basic input/output system, so the computer responds to keystrokes as soon as it is turned on.
The standard keyboard has more than 100 keys, functionally divided into several groups.
The group of alphanumeric keys is intended for entering character information and commands typed by letter. Each key can work in several modes (registers) and, accordingly, can be used to enter several characters.
The group of function keys includes twelve keys located at the top of the keyboard. The functions assigned to these keys depend on the properties of a particular working in this moment programs, and in some cases from properties operating system. It is a common convention for most programs that the F1 key brings up the help system, where you can find help about other keys.
Service keys are located next to the keys of the alphanumeric group. Due to the fact that they have to be used often, they have an increased size. These include SHIFT keys, ENTER, ALT, CTRL, TAB, ESC, BACKSPACE, etc.
Two groups of cursor keys are located to the right of the alphanumeric pad.
Key group additional panel duplicates the action of the numeric and some symbolic keys of the main panel. The appearance of an additional keyboard dates back to the early 80s. At the time, keyboards were relatively expensive devices. The initial purpose of the additional panel was to reduce the wear and tear of the main panel when performing settlement and cash calculations, as well as when managing computer games. Nowadays, keyboards are classified as low-value wearing devices and devices, and there is no essential need to protect them from wear and tear.
Mouse – manipulator type control device. It is a flat box with two or three buttons. Mouse movement on a flat surface is synchronized with the movement of a graphic object (mouse pointer) on the monitor screen.
Unlike the keyboard, the mouse is not a standard control, and the personal computer does not have a dedicated port for it. There is also no permanent dedicated interrupt for the mouse, and the basic input and output facilities do not include software to handle mouse interrupts. In this regard, at the first moment after turning on the computer, the mouse does not work. It needs the support of a special system program - the mouse driver. The mouse driver is designed to interpret the signals coming through the port. In addition, it provides a mechanism for communicating information about the position and state of the mouse to the operating system and running programs.
The computer is controlled by moving the mouse along the plane and by briefly pressing the right and left buttons (clicks). Unlike the keyboard, the mouse cannot be used directly to enter sign information - the control principle is event-driven. Mouse movements and clicks of its buttons are events from the point of view of its driver program. By analyzing these events, the driver determines when the event occurred and where the pointer was at that moment on the screen. This data is passed to the application that the user is currently working with. According to them, the program can determine the command that the user had in mind, and proceed to its execution.
The monitor and mouse combination provides the most modern type user interface, which is called graphical. The user is watching on the screen graphic objects and controls. Using the mouse, he changes the properties of objects and activates controls. computer system, and with the help of the monitor receives a response in graphical form.
Adjustable mouse parameters include: sensitivity (expresses the amount of movement of the pointer on the screen for a given linear movement of the mouse), the functions of the right and left buttons, as well as sensitivity to double tap(maximum time interval at which two mouse clicks are treated as one double click).
Computer network (CS) – a set of computers and terminals connected via communication channels into a single system that meets the requirements of distributed data processing.
In general, under telecommunications network (TS ) understand a system consisting of objects that perform the functions of generating, transforming, storing and consuming a product, called points (nodes) of the network, and transmission lines (communications, communications, connections) that transfer the product between points.
Depending on the type of product - information, energy, mass - information, energy and material networks are distinguished, respectively.
Information network (IS)– a communication network in which the product of generating, processing, storing and using information is information. Traditionally, telephone networks are used to transmit sound information, television is used for images, and telegraph (teletype) is used for text. Nowadays information is becoming more and more widespread. integrated service networks, allowing to transmit sound, image and data in a single communication channel.
Computing network (AC) - an information network, which includes computing equipment. The components of a computer network can be computers and peripheral devices that are sources and receivers of data transmitted over the network.
Aircraft are classified according to a number of criteria.
1. Depending on the distance between network nodes, aircraft can be divided into three classes:
· local(LAN, LAN - Local Area Network) - covering a limited area (usually within the remoteness of stations no more than a few tens or hundreds of meters from each other, less often 1 ... 2 km);
· corporate (enterprise scale ) - a set of interconnected LANs covering the territory where one enterprise or institution is located in one or several closely spaced buildings;
· territorial– covering significant geographic area; Among territorial networks, one can single out regional networks (MAN - Metropolitan Area Network) and global networks (WAN - Wide Area Network), having, respectively, regional or global scales.
The concept of computer networks; local and global networks; network topologies; network operating systems.
Purpose of the lecture:
- to study the hardware and software of local and global networks.
Appearance personal computers required a new approach to the organization of the data processing system, to the creation of new information technologies. There was a need to move from the use of individual computers in centralized data processing systems to distributed data processingnyh in computer network. Subscribers networks can be individual computers, computer complexes, terminals, industrial robots, machine tools with numerical control, etc. Depending on the geographical location of subscribers, computer networks are divided into global, regional And local. Combining global, regional and local computer networks allows you to create multihomed hierarchies, providing powerful tools for processing huge information arrays and access to unlimited information resources.
In the general case, a computer network is represented by a set of three nested subsystems: workstation networks, server networks And basic data network.
The basic requirements that determine the architecture of computer networks are as follows: openness, survivability, adaptability, security information . These requirements are provided by the modular organization of process control in the network, implemented according to a multi-level scheme. The number of levels and the distribution of functions between them significantly affect the complexity of the software of computers included in the network and the efficiency of the network. There is no formal procedure for choosing the number of levels.
Taken as a reference model seven-level scheme: level 1 - physical, at level 2 - canal, at level 3 - network, level 4 - transport, 5 - session, 6 - representative, 7 - applied. Layers 1-3 organize the basic data transmission network as a system that provides reliable data transmission between network subscribers. At level 5, at the request of processes, ports are created for receiving and transmitting messages and connections are organized - logical channels.
The order of implementation of links in the network is regulated protocols.
The basic principles of organizing a computer network determine its main characteristics: operational capabilities, performance, message delivery time and the cost of the services provided.
Information systems built on the basis local computer networks, provide the solution of the following tasks: data storage, data processing, organization of user access to data, transfer of data and the results of their processing to users.
Computer networks implement distributed data processing. Here, data processing is distributed between two objects: client And server. The server provides storage of public data and organizes access to this data. In the process of data processing, the client generates a request to the server to perform complex procedures. The server executes the request and sends the results to the client. This model of a computer network is called archiclient-server textures.
Another computer network model is file server, which starts the operating system and controls the flow of data transmitted over the network. Separate workstations and any shared peripherals (printers, scanners, modems, etc.) are connected to the file server. Each workstation runs its own disk operating system, but unlike a stand-alone personal computer, it contains a network interface card and is physically connected by cables to the file server. The workstation starts network shell, which allows you to use files and programs stored on a file server as easily as those on its own drives. To turn on workstation into the network, shell network operating system is loaded into the beginning of the computer's operating system. The shell retains most of the commands and functions of the operating system and adds local system more features, which gives it flexibility.
On the basis of the distribution of functions, local computer networks are divided into peer-to-peer And two-rank(hierarchical networks or networks with a dedicated server). In a peer-to-peer network, a computer acts as both a client and a server. Peer-to-peer sharing of resources is quite acceptable for small offices with 5-10 users, grouping them into working group. A two-rank network is organized on the basis of a server on which network users register. For modern computer networks is typical mixed a network that unites workstations and servers, with some of the workstations forming peer-to-peer networks, and the other part belonging to dual-rank networks.
The geometric connection diagram (physical connection configuration) of network nodes is called network topology. There are a large number of options for network topologies, the basic ones are tire, ring, star. The local network can use one of the listed topologies. It depends on the number of connected computers, their relative position and other conditions.
Bus topology problems arise in the following cases: when there is a break at any point on the bus; when the network adapter of one of the computers fails and signals with interference are transmitted to the bus; if you need to connect a new computer to the network. The disadvantages of the ring organization are breaks anywhere in the ring, stopping the operation of the entire network; the dependence of the message transmission time on the sequential operation time of each node located between the sender and the recipient; the possibility of unintentional distortion of information due to the passage of data through each node. The combination of basic topologies (hybrid) provides a wide range of solutions that accumulate the advantages and disadvantages of the basic ones.
Different networks have different procedures that describe how to access network channels (data transfer protocols). The most common implementations of access methods are: ethernet, Arcnet And Token- ring.
Access Method ethernet developed by the company Xerox in 1975, is the most popular, as it provides a high data transfer rate and does not exclude the possibility of simultaneous transmission of messages by two or more stations. This access method uses a "common bus" topology.
Access Method Arcnet developed by the firm DatapointCorp. became widespread due to the fact that Arcnet cheaper than hardware ethernet or Token- ring. Arcnet used in local networks with a star topology.
Access Method Token- ring was developed by the company IBM and designed for ring topology networks.
In addition to the problems of creating local computer networks, there is also the problem of expanding (combining) computer networks. A computer network created at a certain stage in the development of an information system may eventually cease to meet the needs of all users. At the same time, the physical properties of signals, data transmission channels, and design features of network components impose severe restrictions on the number of nodes and the geometric dimensions of the network. To join local networks the following devices are used: repeater, bridge, router,Gateway.
Large local networks are combined into global ones. The functioning of global networks is supported by control centers (special computers), which serve only for administrative purposes, keep records, provide users with information regarding network resources, and check network operation. Users communicate with other network subscribers using special communication software. Currently, the largest global network, covering almost all countries of the world, is considered Internet.
Internet provides the exchange of information between all computers that are part of the network connected to it, and provides its users with a variety of various resources. The type of computer and the operating system it uses does not matter.
In order for information to be transmitted between computers, regardless of the communication lines used, the type of computer and software, developed special data transfer protocols. They work on the principle of splitting data into blocks of a certain size (packets), which are sequentially sent to the addressee. There are two main protocols used on the Internet : internet protocol IP And transmission control protocol TCP. Since these protocols are interrelated, one usually speaks of a protocol TCP/ IP.
main cells Internet are local computer networks. If some local network is connected to Internet, then each workstation of this network can also connect to Internet. Computers that connect to Internet, are called host computers.
Each computer connected to the network has its own address. Station addresses are subject to special requirements. The address must be in a format that allows it to be processed automatically, and must carry information about its owner. For this purpose, two addresses are set for each computer: digital IP-the address And domain address. The first of them is more understandable to a computer, the second - to a person. Both of these addresses are equal.
To simplify the communication of network subscribers, its entire address space is divided into separate areas - domains, which in the address system Internet are represented by geographic regions and have a two-letter name. There are domains divided by thematic features, having a three-letter abbreviated name. A computer name includes at least two levels of domains, which are separated from each other by a dot. The top-level domain is indicated on the right, subdomains of the general domain are indicated on the left.
To handle the search path in domains, there are special name servers.
The use of Internet technologies is not necessarily implemented within the framework of a worldwide information network. The technologies used in the global network are also suitable for creating powerful corporate information systems and collaboration systems ( intranet).
Components (protocols, programs, server computers) put together to provide one of the services Internet, are called services(services, services) networks. One of the most important services is Email. Local email systems are characterized by privacy, low cost, and high functionality. There are two main types of local systems: centrallybathroom systems And LAN based systems. There are many email software packages. These include MicrosoftOutlookExpress, MicrosoftMail, NovellgroupWise and others. Email features can be used in Internet. It uses an address system based on the domain address of the computer connected to the Internet.
Additional information on the topic can be found in .












































Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-1.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> Computer networks and telecommunications Lecture 7 ">
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-2.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> The purpose of teaching the basics of computer networks"> Цель обучения основам компьютерных сетей и телекоммуникаций - обеспечить знание теоретических и практических основ в организации и функционировании компьютерных сетей и телекоммуникаций, умение применять в профессиональной деятельности распределенные данные, прикладные программы и ресурсы сетей.!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-3.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> Tasks q familiarization with the main trends in the development of methods and"> Задачи q знакомство с основными тенденциями развития методов и технологий компьютерных сетей; q знакомство с механизмами передачи данных по каналам связи; q знакомство с возможными ресурсами ЛВС; q знакомство с сервисом сети Іnternet.!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-4.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> Computer network"> Компьютерная сеть Это совокупность компьютеров и телекоммуникационного оборудования, обеспечивающая информационный обмен компьютеров в сети. Основное назначение компьютерных сетей - обеспечение доступа к распределенным ресурсам.!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-5.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> Telecommunications (Greek tele - far, far and Latin communicatio - communication) -"> Телекоммуникации (греч. tele - вдаль, далеко и лат. communicatio - общение) - это передача и прием любой информации (звука, изображения, данных, текста) на расстояние по различным электромагнитным системам.!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-6.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> A telecommunications network is a system technical means, through which "> Telecommunication network is a system of technical means through which telecommunications are carried out.
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-7.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> Telecommunication networks include:"> К телекоммуникационным сетям относятся: Радиосети Телевизионн Телефонные (передача ые сети Компьютер (передача сети голосовой ные сети голоса и (передача информаци (для изображения голосовой и - - передачи информаци широковещ данных). широковещат и). ательные услуги).!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-8.jpg" alt="(!LANG:>Computer network classification Computer networks By territorial distribution"> Классификация компьютерных сетей Компьютерные сети По территориальной распространённости По типу функционального взаимодействия По типу сетевой топологии По типу среды передачи По скорости передачи данных По используемым сетевым моделям!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-9.jpg" alt="(!LANG:>By territorial distribution Wearable Global Personal"> По территориальной распространённости Нательная Глобальная Персональная Компьютерные сети Городская Локальная Кампусная!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-10.jpg" alt="(!LANG:>BAN (Body Area Network) - wireless network of wearable"> Нательная компьютерная сеть BAN (англ. Body Area Network) - беспроводная сеть надеваемых компьютерных устройств. BAN устройства могут быть встроены в тело, имплантированы, прикреплены к поверхности тела в фиксированном положении или совмещены с устройствами, которые люди носят в различных местах (карманах, на руке или в сумках).!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-11.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> PAN (Personal Area Network) is"> Персональная сеть PAN (англ. Personal Area Network) - это сеть, построенная «вокруг» человека. PAN представляет собой компьютерную сеть, которая используется для передачи данных между устройствами, такими как компьютеры, телефоны, планшеты и персональные карманные компьютеры (КПК).!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-12.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> Local Area Networks LAN)"> Локальные сети LAN (англ. Local Area Network) обеспечивают наивысшую скорость обмена информацией между компьютерами. Типичная локальная сеть занимает пространство в одно 2 здание. Протяженность локальных сетей составляет около одного километра. Их основное назначение состоит в объединении пользователей (как правило, одно компании или организации) для совместной работы.!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-13.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> Campus Area Network)"> Кампусная сеть CAN (англ. Campus Area Network) - это группа локальных сетей, развернутых на компактной территории (кампусе) какого-либо учреждения и обслуживающие одно это учреждение - университет, промышленное предприятие, порт, оптовый склад и т. д. При этом !} network hardware(switches, routers) and transmission media (optical fiber, copper plant, Cat 5 cables, etc.) of data belongs to the tenant or owner of the campus, enterprise, university, government, and so on.
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-14.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) allows"> Городские сети MAN (англ. Metropolitan Area Network) позволяют взаимодействовать на территориальных образованиях меньших размеров и работают на скоростях от средних до высоких. Они меньше замедляют передачу данных, чем глобальные, но не могут обеспечить высокоскоростное взаимодействие на больших расстояниях. Протяженность городских сетей находится в переделах от нескольких километров до десятков и сотен километров.!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-15.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> WANs (Wide Area Network)"> Глобальные сети WAN (англ. Wide Area Network) позволяют организовать взаимодействие между абонентами на больших расстояниях. Эти сети работают на относительно !} low speeds and can introduce significant delays in the transmission of information. The length of global networks can be thousands of kilometers. Therefore, they are somehow integrated with national networks.
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-16.jpg" alt="(!LANG:>By functional interaction type Computer networks One"> По типу функционального взаимодействия Компьютерные сети Одно ранговая Клиент-сервер сеть!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-17.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> Client-Server This is a computing or network architecture in which"> Клиент-сервер Это вычислительная или сетевая архитектура, в которой задания или сетевая нагрузка распределены между поставщиками услуг, называемыми серверами, и заказчиками услуг, называемыми клиентами. Фактически клиент и сервер - это программное обеспечение. Обычно эти программы расположены на разных вычислительных машинах и взаимодействуют между собой через вычислительную сеть посредством сетевых протоколов, но они могут быть расположены также и на одной машине.!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-18.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> Peer-to-Peer Network Peer-to-Peer Network Architecture"> Одноранговая сеть О дноранговая сетевая архитектура - стабильно набирающий популярность способ организации высокоуровнего сетевого взаимодействия, где все узлы сети обладают равными правами и выступают поставщиками и потребителями сетевых сервисов одновременно.!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-19.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> By network topology type Star Mesh Double"> По типу сетевой топологии Звезда Ячеистая Двойное Решетка кольцо Кольцо Дерево Компьюте Шина рные сети Fat Tree!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-20.jpg" alt="(!LANG:>"> По типу сетевой топологии Топология типа общая ши на, представляет собой общий кабель (называемый шина или магистраль), к которому подсоединены все рабочие станции. На концах кабеля находятся терминаторы, для предотвращения отражения сигнала. Кольцо - топология, в которой каждый компьютер соединён линиями связи только с двумя другими: от одного он только получает информацию, а другому только передаёт.!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-21.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> By type of network topology Grid (Grid network , sometimes"> По типу сетевой топологии Решётка (Grid network , иногда также mesh, например 3 D-mesh) - понятие из теории организации компьютерных сетей. Это топология, в которой узлы образуют регулярную многомерную решётку. Дерево - это топология сетей, в которой каждый узел более высокого уровня связан с узлами более низкого уровня звездообразной связью, образуя комбинацию звезд. Также дерево называют иерархической звездой.!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-22.jpg" alt="(!LANG:>"> По типу сетевой топологии Двойное кольцо - топология, построенная на двух кольцах. Первое кольцо - основной путь для передачи данных. Второе - !} backup way, duplicating the main one. Star - the basic topology of a computer network in which all computers in the network are connected to a central node (usually a switch), forming a physical network segment. Mesh topology - network topology of a computer network, built on the principle of cells, in which network workstations are connected to each other and are able to take on the role of a switch for other participants.
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-23.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> Fat tree network (thick tree) - computer network topology,"> Сеть fat tree (утолщенное дерево) - топология компьютерной сети, изобретённая Чарльзом Лейзерсоном из MIT, является дешевой и эффективной для суперкомпьютеров. В отличие от классической топологии дерево, в которой все связи между узлами одинаковы, связи в утолщенном дереве становятся более широкими (толстыми, производительными по пропускной способности) с каждым уровнем по мере приближения к корню дерева. Часто используют удвоение пропускной способности на каждом уровне.!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-24.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> By media type Computer networks Wired networks"> По типу среды передачи Компьютерные сети Проводные сети Беспроводные сети!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-25.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> Wired networks Wireless networks"> Проводные сети Беспроводные сети Основа всего: кабели. Во Это вычислительная сеть, всех сетевых стандартах основанная определены необходимые на беспроводном (без условия и характеристики использования кабельной проводки) принципе, используемого кабеля, полностью соответствующая такие как полоса стандартам для обычных пропускания, волновое проводных сетей. В качестве сопротивление носителя информации в (импеданс), удельное таких сетях могут выступать затухание сигнала, радиоволны СВЧ-диапазона. помехозащищенность и другие.!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-26.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> Types of cables There are two fundamentally different types of network cables:"> Виды кабелей Существуют два принципиально разных вида сетевых кабелей: медные и оптоволоконные. Кабели на основе медных проводов, в свою очередь, делятся на коаксиальные и !} twisted pair: Coaxial cable is a central conductor surrounded by a dielectric layer (insulator) and a metal braid screen, which also acts as a second contact in the cable. A twisted pair consists of several (usually 8) pairs of twisted conductors. Twisting is used to reduce interference from both the pair itself and external ones that affect it. A pair twisted in a certain way has such a characteristic as wave resistance.
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-27.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> A fiber optic cable consists of one or more fibers enclosed in sheaths,"> Оптоволоконный кабель состоит из одного или нескольких волокон, заключенных в оболочки, и бывает двух типов: одномодовый и многомодовый. Их различие в том, как свет распространяется в волокне в одномодовом кабеле все лучи проходят одинаковое расстояние и достигают приемника одновременно, а в многомодовом сигнал может размазаться.!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-28.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> By data rate Computer networks"> По скорости передачи данных Компьютерные сети высокоскоростные низкоскоростные среднескоростные (свыше 100 (до 10 Мбит/с), (до 100 Мбит/с), Мбит/с);!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-29.jpg" alt="(!LANG:>According to network models used OSI computer networks"> По используемым сетевым моделям Компьютерные сети OSI TCP/IP!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-30.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> Network Model This is a network protocol interaction model. A"> Сетевая модель Это модель взаимодействия сетевых протоколов. А протоколы в свою очередь, это стандарты, которые определяют каким образом, будут обмениваться данными различные программы.!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-31.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> OSI Open System Interconnection"> OSI Open System Interconnection - взаимодействие открытых систем, ВОС - это 7 -уровневая логическая модель работы сети. Модель OSI реализуется группой протоколов и правил связи, организованных в несколько уровней: 1. на физическом уровне определяются физические (механические, электрические, оптические) характеристики линий связи; 2. на канальном уровне определяются правила использования физического уровня узлами сети; 3. сетевой уровень отвечает за адресацию и доставку сообщений;!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-32.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> OSI 4. The transport layer controls the order in which the components"> OSI 4. транспортный уровень контролирует очередность прохождения компонентов сообщения; 5. задача сеансового уровня - координация связи между двумя прикладными программами, работающими на разных рабочих станциях; 6. уровень представления служит для преобразования данных из внутреннего формата компьютера в формат передачи; 7. прикладной уровень является пограничным между !} application program and other levels - provides a convenient interface for connecting user network programs.
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-33.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> TCP / IP Transmission Control Protocol /"> TCP / IP Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol Основоположники: Robert Kahn, Vinton Cerf (1972 – 1974) Основан на использовании IP-адресов вида: a. b. c. d (четыре числа от 0 до 255) для любого хоста (компьютера) в сети и пакетов (packets) фиксированного размера, содержащих адрес получателя Используется в Интернете Более общее современное название: Internet Protocol Suite (различаются более !} a new version– IPv 6 and older – IPv 4) Another option: UDP/IP (UDP is an asynchronous transport protocol that exchanges datagrams - variable length byte arrays); less reliable but more Fast Speed TCP/IP is not always satisfactory. To optimize communication between network nodes, Distributed Hash Tables (DHT) are used - distributed hash tables and Peer-to-Peer (P 2 P) Networks - peer-to-peer networks. They implement their own system of host names and their faster search than using TCP / IP protocols 33
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-34.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> TCP / IP TCP/IP - contains 4 layers: channel"> TCP / IP TCP/IP - содержит 4 уровня: канальный уровень (link layer), сетевой уровень (Internet layer), транспортный уровень (transport layer), прикладной уровень (application layer).!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-35.jpg" alt="(!LANG:>Model levels">!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-36.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> A protocol stack is a hierarchically organized set of"> Стек протоколов - это иерархически организованный набор сетевых протоколов, достаточный для организации взаимодействия узлов в сети. Протоколы работают в сети одновременно, значит работа протоколов должна быть организована так, чтобы не возникало конфликтов или незавершённых операций. Поэтому стек протоколов разбивается на иерархически построенные уровни, каждый из которых выполняет конкретную задачу - подготовку, приём, передачу данных и последующие действия с ними.!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-37.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> Network protocol This is a set of rules and actions (queues of actions) that allows realize"> Сетевой протокол Это набор правил и действий (очерёдности действий), позволяющий осуществлять соединение и обмен данными между двумя и более включёнными в сеть устройствами.!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-38.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> Protocol 1. HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer"> Протокол 1. HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol) - это протокол передачи гипертекста. !} HTTP protocol used when sending Web pages between computers connected to the same network. 2. FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is a protocol for transferring files from a special file server to a user's computer. FTP allows a subscriber to exchange binary and text files with any computer on the network. By establishing a connection with a remote computer, the user can copy a file from remote computer to your own or copy the file from your computer to a remote one.
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-39.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> Protocol 3. POP 3 (Post Office Protocol) is"> Протокол 3. POP 3 (Post Office Protocol) - это стандартный протокол почтового соединения. Серверы POP обрабатывают входящую почту, а протокол POP предназначен для обработки запросов на получение почты от клиентских почтовых программ. 4. SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) - протокол, который задает набор правил для передачи почты. Сервер SMTP возвращает либо подтверждение о приеме, либо сообщение об ошибке, либо запрашивает дополнительную информацию.!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-40.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> Protocol 5. TELNET is a remote access protocol. TELNET"> Протокол 5. TELNET - это протокол удаленного доступа. TELNET дает возможность абоненту работать на любой ЭВМ находящейся с ним в одной сети, как на своей собственной, то есть запускать программы, менять режим работы и так далее. На практике возможности ограничиваются тем уровнем доступа, который задан администратором удаленной машины. 6. DTN - протокол, предназначенный для сетей дальней космической связи IPN, которые используются NASA.!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-41.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> Protocol 7. DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration)"> Протокол 7. DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol - протокол динамической настройки узла) - !} network protocol, which allows computers to automatically obtain an IP address and other settings required to operate on a TCP/IP network. This protocol works on a client-server model. 8. Internet Protocol (IP, literally "internet protocol") is a routable protocol of the network layer of the TCP / IP stack. It was IP that became the protocol that united individual computer networks in worldwide network Internet. An integral part of the protocol is network addressing.
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-42.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> IP address and Netmask Each computer"> IP – адрес и Маска сети У каждого компьютера в сети Интернет есть свой уникальный адрес - Uniform Resource Locator (URL). Цифровые адреса состоят из четырех целых десятичных чисел, разделённых точками, каждое из этих чисел находится в интервале 0… 255. Пример: 225. 224. 196. 10.!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-43.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> IP Address and Netmask Maximum amount IP"> IP - Address and Netmask The maximum number of IP addresses that can be used in a subnet of a certain size is called subnet mask (subnet mask). In TCP / IP networking terminology, a subnet mask or netmask is a bit mask that determines which part of a host's IP address refers to the address of the network, and what part refers to the address of the host itself on that network.For example, a host with an IP address of 12.34.56.78 and a subnet mask of 255.0 is on the network 12.34.56 .0/24
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-44.jpg" alt="(!LANG:> IP address and Netmask Internet document address"> IP – адрес и Маска сети Адрес документа в Интернете состоит из следующих частей: 1. протокол, чаще всего HTTP (для Web-страниц) или FTP (для файловых архивов) 2. знаки: //, отделяющие протокол от остальной части адреса 3. доменное имя (или IP-адрес) сайта 4. каталог на сервере, где находится файл 5. имя файла Пример адреса: http: //testedu. ru/test/istoriya/11 -klass/!}
Src="https://present5.com/presentation/3/156029098_452833218.pdf-img/156029098_452833218.pdf-45.jpg" alt="(!LANG:>Thank you for your attention!!!">!}
Ontopsychology has developed a whole series of rules, recommendations for the formation of the personality of a manager, businessman, leader top level which are already subject to almost any leader who is able to realize their usefulness and necessity. From the entire set of these recommendations, it is advisable to highlight and summarize the following:
1. No need to destroy your image with dishonest deeds, fraud.
2. Do not underestimate the business partner, consider him dumber than yourself, try to deceive him and offer a low-level market system.
3. Never associate with those who are unable to arrange their own affairs.
If you have a team member who fails in all his undertakings, then you can predict that in a few years you will also face a collapse or big losses. Pathological losers, even if they are honest and intelligent, are characterized by unconscious programming, immaturity and unwillingness to take responsibility for their lives. This is social psychosomatics.
4. Never hire a fool. It is necessary to stay away from him in work and in personal life. Otherwise, unpredictable consequences for the leader may occur.
5. Never take on your team someone who is frustrated because of you.
Do not be guided in the selection of personnel by devotion, deceived by flattery or sincere love. These people may be insolvent in difficult official situations. It is necessary to choose those who believe in their work, who use work to achieve their own interests, who want to make a career, improve their financial situation. By excellently serving the leader (owner), he can achieve all these goals, satisfy personal egoism.
6. In order to earn, to prosper, one must be able to serve partners, cultivate one's own manner of behavior.
The main tactic is not to please the partner, but to study his needs and interests and take them into account when business communication. It is necessary to build value relationships with the carriers of wealth and success.
7. Never mix personal and business relationships, personal life and work.
An excellent leader should be distinguished by refined taste in his personal life and the highest rationality, an unusual style in the business sphere.
8. A real leader needs the mentality of a single person who owns the absolute right to the final idea.
It is known that the biggest projects of real leaders owe their success to his silence.
9. When making a decision, it is necessary to focus on global success for the company, i.e. when the result will benefit everyone who works for the leader and whom he leads.
In addition, in order for the solution to be optimal, it is necessary:
preservation of everything positive that has been created so far;
cautious rationality based on available means;
rational intuition (if, of course, it is inherent in the leader, because this is already the quality of the leader - leader)
10. The law must be observed, circumvented, adapted to it and used.
This formulation, despite its inconsistency, has a deep meaning and in any case means that the activities of the leader must always be in the right field, but this can be done in different ways. The law is the power structure of society, the connective tissue between the leader and others who are physically inclined "for" or "against" him.
11. You should always follow the plan ahead of the situation, do not pay too much attention to erroneous action.
In the absence of the strictest control on the part of the leader, the situation objectifies him and, ultimately, despite the fact that he could do everything, he does nothing and stress develops rapidly.
12. It is always necessary to create everyday aesthetics, because. achieving greatness in small things leads to great goals.
The whole is achieved through the orderly reconciliation of the parts. Objects left in disorder are always protagonists. The leader, depriving himself of aesthetics, robs his aesthetic ability.
To lead effectively, one must have proportionality in 4 areas: individual personal, family, professional and social.
13. In order to avoid conflicts that lie in wait for us every day, we must not forget about 2 principles: avoid hatred and revenge; never take someone else's that does not belong to you in accordance with the intrinsic value of things.
In general, all managers, merchants and businessmen, regional and party leaders can be divided into 2 classes:
The first class consists of persons who, at their core, pursue personal and (or) public humanistic, moral goals in their activities.
The second class pursues personal and (or) public selfish, monopolistic goals (in the interests of a group of persons).
The first class of people is able to realize the need to use the rules and recommendations discussed above. A significant part of these people, by virtue of their decency and rational intuition, already uses them, even without being familiar with these recommendations.
The second group of people, who can be conditionally called new Russians (“NRs”), are incapable of recognizing this problem due to their personal qualities and due to the absence, unfortunately, of a civilized socio-economic environment in the country:
Communication with this group is whole line negative sides, because "NR" have a number of negative professionally important qualities (tab. 23).
Table 23
Negative professionally important qualities (PVC) "NR"
| Psychological qualities | Psychophysiological qualities |
| 1. Irresponsibility | 1. Unproductive and illogical thinking |
| 2. Aggressiveness | 2. Conservatism of thinking |
| 3. Permissiveness | 3. Lack of efficiency of thinking in non-standard situations |
| 4. Impunity | 4. Instability of attention. |
| 5. The vagueness of the concept of “legality of actions” | 5. Bad RAM |
| 6. Inflated professional self-esteem | 6. Inability to coordinate various ways perception of information. |
| 7. Categorical | 7. Slow response to changing situations |
| 8. Overconfidence | 8. Inability to act unconventionally |
| 9. Low professional and interpersonal competence | 9. Lack of flexibility in decision making |
These negative aspects of communication cause a number of conflicts that do not always have a personal character and, due to the mass nature and often specificity, give rise to a number of already social, departmental and state problems and, ultimately, affect the psychological safety of leaders as individuals and even national country's security. This situation can be reversed only through the purposeful formation of a civilized socio-economic environment with a focus on humanistic, moral, national goals and widespread promotion of the achievements of ontopsychology in the field of shaping the personality of top-level leaders. The ultimate goal of this process is to change the value orientations of the widest circles of the population. National security is obviously affected by the ratio of the number of first and second class people. It is possible that at present the number of persons in the second group is greater than in the first. At what excess of the number of persons in the first class over the second can national security be ensured is a difficult question. Perhaps, in this case, the typical condition for the reliability of static hypotheses (95%) should be fulfilled. In any case, when the above activities are carried out, the number of people in the first class will increase, and the second - will decrease, and this process itself will already have a beneficial effect.
Mironova E.E. Collection of psychological tests. Part 2.
Computer networks and telecommunications
A computer network is an association of several computers for the joint solution of information, computing, educational and other problems.
Computer networks have given rise to significantly new information processing technologies - network technologies. In the simplest case, network technologies allow the sharing of resources - mass storage devices, printing devices, Internet access, databases and data banks. The most modern and promising approaches to networks are associated with the use of a collective division of labor in joint work with information - the development of various documents and projects, the management of an institution or enterprise, etc.
The simplest type of network is the so-called peer-to-peer network that provides communication between personal computers of end users and allows sharing disk drives, printers, files. More developed networks, in addition to end-user computers - workstations - include special dedicated computers - servers . Server- a computer that performs special functions on the network to serve other computers on the network - workers antsy. There is different types servers: file, telecommunication servers, servers for mathematical calculations, database servers.
Very popular today and extremely promising technology information processing in the network is called "client - server". The "client - server" methodology assumes a deep separation of the functions of computers in the network. At the same time, the function of the "client" (which is understood as a computer with the corresponding software) includes
Providing user interface, focused on certain production duties and user powers;
Formation of requests to the server, and not necessarily informing the user about it; ideally, the user does not delve into the technology of communication between the computer he works on and the server at all;
Analysis of server responses to requests and their presentation to the user. The main function of the server is to perform specific actions on requests.
client (for example, solving a complex mathematical problem, searching for data in a database, connecting a client to another client, etc.); however, the server itself does not initiate any interactions with the client. If the server addressed by the client is unable to solve the problem due to lack of resources, then ideally it finds another, more powerful server itself and transfers the task to it, becoming, in turn, a client, but without informing about it unnecessarily initial client. Note that the "client" is not the server's remote terminal at all. The client can be a very powerful computer, which, by virtue of its capabilities, solves problems independently.
Computer networks and network technologies for information processing have become the basis for building modern information systems. The computer should now be considered not as a separate processing device, but as a “window” on computer networks, a means of communication with network resources and other network users.
Local area networks (LAN computers) unite a relatively small number of computers (usually from 10 to 100, although occasionally there are much larger ones) within the same room (training computer class), building or institution (for example, a university). Traditional name - local area network (LAN)
Distinguish:
Local area networks or LANs (LAN, Local Area Network) - networks that are geographically small in size (a room, a floor of a building, a building or several nearby buildings). As a data transmission medium, as a rule, a cable is used. Recently, however, wireless networks have been gaining popularity. The proximity of computers is dictated by the physical laws of signal transmission over the cables used in the LAN or the power of the wireless signal transmitter. LANs can unite from several units to several hundred computers.
The simplest LAN, for example, may consist of two PCs connected by cable or wireless adapters.
Internetworks or network complexes are two or more LANs connected by special devices to support large LANs. They are essentially networks of networks.
Wide area networks - (WAN, Wide Area Network) LANs connected by means of remote data transmission.
Corporate networks- global networks administered by one organization.
From the point of view of the logical organization of the network, there are peer-to-peer and hierarchical.
The creation of automated enterprise management systems (ACS) had a great influence on the development of drugs. ACS includes several automated workstations (AWP), measuring complexes, control points. Another important field of activity in which drugs have proven their effectiveness is the creation of classes for educational computer science(KUVT).
Due to the relatively short lengths of communication lines (as a rule, no more than 300 meters), information can be transmitted via LAN in digital form at a high transmission rate. At long distances, this method of transmission is unacceptable due to the inevitable attenuation of high-frequency signals, in these cases it is necessary to resort to additional technical (digital-to-analog conversions) and software (error correction protocols, etc.) solutions.
Feature LS- the presence of a high-speed communication channel connecting all subscribers for transmitting information in digital form. Exist wired and wireless channels. Each of them is characterized by certain values of parameters that are essential from the point of view of LAN organization:
Data transfer rates;
Maximum line length;
Noise immunity;
mechanical strength;
Convenience and ease of installation;
Costs.
Currently commonly used four types of network cables:
Coaxial cable;
Unprotected twisted pair;
Protected twisted pair;
Fiber optic cable.
The first three types of cables transmit an electrical signal over copper conductors. Fiber optic cables transmit light over glass fiber.
Wireless communication on microwave radio waves can be used to organize networks within large premises such as hangars or pavilions, where the use of conventional communication lines is difficult or impractical. In addition, wireless lines can connect remote segments of local networks at distances of 3 - 5 km (with a wave channel antenna) and 25 km (with a directional parabolic antenna) under the condition of direct visibility. Organizations wireless network significantly more expensive than normal.
For the organization of training LANs, twisted pair is most often used, like itself! cheap, since the requirements for data transfer rate and line length are not critical.
To connect computers using LAN links, you need network adapters(or, as they are sometimes called, network posters you). The most famous are: adapters of the following three types:
ArcNet;