Gives the file extension. Why do files need name extensions - basic types
This is one of the common ways that a user or computer software can determine the type of data stored in a file.
The extension is usually separated from the main part of the file name by a dot . In CP/M and MS-DOS operating systems, the length of the extension was limited to three characters, in modern operating systems this restriction is not. Sometimes multiple extensions can be used in succession, such as ".tar.gz".
In the FAT16 file system, the filename and extension were separate entities, and the dot separating them was not really part of the full filename and served only to visually separate the filename from the extension. In the FAT32 and NTFS file systems, the dot has become a common legal character in a filename, so restrictions on the number of dots in a filename on these systems and their locations have been lifted (with some exceptions, such as all trailing dots in filenames are simply discarded). So the standard search pattern *.* has no practical meaning anymore, it is enough to ask * , since the dot symbol now falls under the concept of any symbol.
Some operating systems or file managers may map file extensions to applications. When a user opens a file with a registered extension, the program corresponding to that extension is automatically launched. Some extensions indicate that the file itself is a program.
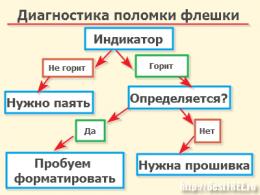
Pointing Accuracy
Sometimes the extension specifies the format only in general (for example, the .doc extension was used for many different text formats - both plain and formatted; and the "txt" extension does not give any information about what encoding the text in the file is), due to what you need to use and other ways to determine the format.
Sometimes the extension specifies only one of the formats used in the file (for example, the ".ogg" extension was originally used for all files in the Ogg format, regardless of the codecs that encoded the data contained in the Ogg container). Also, the extension usually does not indicate the version of the format (for example, files in different versions of XHTML may use the same extensions).
Other ways to specify the format
- On some operating systems and file systems (such as HFS), file format information is stored on the file system itself.
- Magic numbers are sequences of bytes within the files themselves.
- Shebang ( English) - in Unix-like operating systems, it is placed at the beginning of the executable file to indicate the interpreter that should be called when this file is run. Consists of a comment character (#) followed by an exclamation mark (!), followed by the command to be executed with the given file as an argument.
see also
Links
- file-extensions.org
- Dot What? (English)
- Filext
- Wotsit (English)
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010 .
See what "File name extension" is in other dictionaries:
file name extension- The part of the filename following the dot. Topics Information Technology in general EN filename extension ... Technical Translator's Handbook
DOC or .doc (from English document) filename extension used for files representing text, with or without markup. The .DOC extension was often used to denote plain text files without formatting, but later ... Wikipedia
This term has other meanings, see ECW (disambiguation). ECW (Enhanced Compression Wavelet) is a proprietary raster image file format optimized for storing aerial and satellite imagery using ... ... Wikipedia
File extensions are a privilege predominantly of operating systems with GUI. Their main purpose is to indicate operating system which program should be called to open a specific file.
What is a file name extension?
File name extension, (file type, file format) is a sequence of characters that helps Windows understand what kind of data is contained in a file and what program should open it. This sequence of characters is called an extension because it appears at the end of the filename, following the dot. In the file name myfile.txt , the extension is txt . It tells Windows that this is a text file that can be opened by programs associated with this extension, such as WordPad or Notepad.
How can I configure the association of programs with a file name extension?
Each program installed on your computer can open one or more specific types of files, each recognized by its file name extension. If any type of file can be opened by more than one program installed on the computer, then one of them is set to be used by default. To change the program that automatically opens the file type, see the post
What is the maximum length of a filename?
Windows generally limits filenames to 260 characters. But the actual filename should be shorter because the full path is included in this number (for example, C:\Program Files\filename.txt). Therefore, sometimes you may encounter an error when copying a file with a very long name to a folder that has a longer path than the current folder.
What characters cannot be used in a file name?
The following characters cannot be used in the file name: \ / ? : * " > < |
How to see filename extension?
By default, Windows hides filename extensions to make filenames easier to read, but you can make extensions visible. additional information cm. post Show or hide file name extensions.
How to change filename extension?
Generally, you should not change file name extensions, as this may make it impossible to open or modify the file. However, sometimes changing the filename extension can be useful—for example, when you want to turn a text file (.txt) into an HTML file (.htm) so that it can be viewed in a web browser. To change the filename extension, first make sure the extensions are displayed. Then click desired file right click mouse and select Rename . Delete the filename extension, type the new extension, and then press Enter. Windows will warn you that after you change the file name extension, the file may not work properly. If you are sure that the program you are using recognizes the extension you entered, click Yes to confirm the change.
Let's not talk about all kinds of extensions that point to executable files, since the operating system's command interpreter is also a kind of program that works with files that have a mask, for example, .COM; .EXE; .bat; .CMD; .VBS.
Executable file extensions.
Most common file extensions in Windows
The extensions most commonly found on a computer are usually three-character sequences of letters and numbers that help the OS start up right away. desired program to display,
For instance,
Lossless audio files
(lossless compressed audio files) can have the extension flac, ape or wav.
Among the most popular image storage formats the following are used:
1.JPEG- the most popular format for storing bitmap images (drawings, photographs, etc.). This format implies a high degree of compression of the contained information, which ensures a relatively small size of JPEG files. In this case, compressing photos without quality loss, unfortunately, is not impossible. At the same time, to post photos on the Internet or to send by e-mail, it is advisable to change the photo format to JPEG. This is an economical and convenient format for storing raster information. Supports 16.7 million colors.
2.BMP is a standard graphics file format for Windows. As a rule, the BMP format has drawings made in Paint editor, or, for example, the standard "wallpaper" for the desktop. Photos in BMP format are stored uncompressed and can take up a lot of disk space. In this regard, it is often necessary to change the photo format to a more ergonomic one (JPEG, TIF, GIF).
3.TIF- a raster graphics format that allows you to compress images without loss of quality. Supports 16.7 million colors, is considered a standard format for data exchange between computers. It is popular among professionals, for example, among users of digital cameras.
4. GIF- Literally translated as "graphic data exchange format". Files stored in the GIF format are small and can be made up of multiple "frames", allowing you to create simple animations. The main disadvantage of GIF is the limited color set of this format. Therefore, to store multi-color images, it is better to change the photo format to JPEG or TIF.
Vector images
The extension depends on the program in which they are made - for example,
AI( Adobe Illustrator), CDR (Corel Draw), CGM (Computer Graphics Metafile), EPS (Encapsulated Postscript format),
PS (PostScript), SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics), WMF (Windows Metafile), EMF (Extended Metafile)
Animation
APNG (Animated PNG), Autodesk Animation (.fli/.flc), Animated GIF, Adobe Flash(.swf) and others
Text Documents
text file (.txt), AmigaGuide (.guide), OpenOffice.org/StarOffice Writer (.sxw) (open text format),
TeX (.tex), Texinfo (.info), WordPerfect (.wpd), Microsoft Word(.doc, .docx, .docm) (Microsoft protected format, changes frequently, quasi-standard)
Internet (Web pages)
- Static
- HTML - (.html, .htm) - HyperText Markup Language
- XML - (.xml) - Extensible Markup Language (eXtensible Markup Language)
- XHTML - (.xhtml, .xht) - extensible hypertext markup language (eXtensible HyperText Markup Language)
- MHTML - (.mht, .mhtml) - archived HTML (web archive), stores all web page data (text, images, etc.) in one large file packed according to the MIME standard (MIME HTML)
- dynamically generated
- ASP - (.asp) - active server pages from Microsoft ( Active Server Page)
- ASPX - (.aspx) - Active Server Pages based on .NET from Microsoft (Active Server Page .NET)
- ADP - AOLserver Dynamic Page
- BML - (.bml) - Better Markup Language (templating)
- CFM - (.cfm) - ColdFusion Interpreted Scripting Programming Language
- iHTML - (.ihtml) - Inline HTML
- JSP - (.jsp) - JavaServer Pages
- Lasso - (.las, .lasso, .lassoapp)
- PL - (.pl) - Perl programming language
- PHP - (.php, .phtml) - abbreviation for PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor, was originally an abbreviation for Personal Home Page
- SSI - (.shtml, .stm, .shtm) - HTML along with Server Side Includes
Table of the most common extensions:
| Extension | File type | Example |
| exe | programs | ACDSee9.exe |
| com | Command.com | |
| doc | documents (Microsoft Word) | Letter.doc |
| xls | tables(Microsoft Excel) | Catalog.xls |
| txt | text documents | text.txt |
| ppt | presentations (Microsoft PowerPoint) | Presentation.ppt |
| htm | web pages | Book.htm |
| html | Book.html | |
| hlp | reference | Windows.hlp |
| bmp | drawing, photography | Figure.bmp |
| jpg | Photo.jpg | |
| tif | Nature.tif | |
| gif | Figure.gif | |
| mp3 | Music | Song.mp3 |
| mpeg | video | Movie.mpeg |
| avi | clip.avi | |
| zip | ZIP archive | Abstract.zip |
| rar | WinRAR archive | Abstract.rar |
The extension can be longer than 3 characters per modern Windows, and in Linux its presence is not required at all.
In general, file extensions in Windows are often application specific, and open third party application files with this extension may be difficult or even impossible. So, for example, the psd extension has files created in a graphics editor Adobe Photoshop(however, this program allows you to save the finished file in almost any graphic format). Text files created in Microsoft Word can be recognized by the doc extension (docx for new versions of the program), and text editor Open Office works with the odt format. Also text files may have txt or rtf resolution.
How to find out,
What types of files does your operating system work with?
Go to Conductor, in the drop down menu Service select item Folder properties

and in the dialog box that opens, go to the tab File types.

On this tab there will be a table in two columns - the file extension in Windows and the corresponding .
!!! Important
If your computer is set up to show file extensions, then when you change the name of a file, leave the extension as it is. That is, change the file name to a dot. If you change the extension, the file may then stop opening. Remember this!
strana-sovetov.com
21.01.2018
What are the types of files. File name extensions
Every file on a computer stores data of a certain type. For example, it can be textual information, programming codes, image, sound or something else. Intuitively, you already understand what a file extension is. Therefore, today we will fill in the gaps in knowledge and try to delve deeper into the topic.
Definition
The extension is the second part of the filename after the dot. As a rule, it consists of 2-4 characters. This designation simplifies the operation of the operating system, telling it exactly what information is contained in the document and what program to use to open the file.
Text Documents
text file (.txt), AmigaGuide (.guide), OpenOffice.org/StarOffice Writer (.sxw) (open text format),
TeX (.tex), Texinfo (.info), WordPerfect (.wpd), Microsoft Word (.doc, .docx, .docm) (Microsoft protected format, changes frequently, quasi-standard)
Internet (Web pages)
- Static
- HTML - (.html, .htm) - HyperText Markup Language
- XML - (.xml) - extensible markup language (eXtensible Markup Language)
- XHTML - (.xhtml, .xht) - extensible hypertext markup language (eXtensible HyperText Markup Language)
- MHTML - (.mht, .mhtml) - archived HTML (web archive), stores all web page data (text, images, etc.) in one large file packed according to the MIME standard (MIME HTML)
- dynamically generated
- ASP - (.asp) - active server pages from Microsoft (Active Server Page)
- ASPX - (.aspx) - Active Server Pages based on .NET from Microsoft (Active Server Page .NET)
- ADP - AOLserver Dynamic Page
- BML - (.bml) - Better Markup Language (templating)
- CFM - (.cfm) - ColdFusion interpreted scripting programming language
- iHTML - (.ihtml) - Inline HTML
- JSP - (.jsp) - JavaServer Pages
- Lasso - (.las, .lasso, .lassoapp)
- PL - (.pl) - Perl programming language
- PHP - (.php, .phtml) - abbreviation for PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor, was originally an abbreviation for Personal Home Page
- SSI - (.shtml, .stm, .shtm) - HTML along with Server Side Includes
Table of the most common extensions:
| Extension | File type | Example |
| exe | programs | ACDSee9.exe |
| com | Command.com | |
| doc | documents (Microsoft Word) | Letter.doc |
| xls | tables(Microsoft Excel) | Catalog.xls |
| txt | text documents | text.txt |
| ppt | presentations (Microsoft PowerPoint) | Presentation.ppt |
| htm | web pages | Book.htm |
| html | Book.html | |
| hlp | reference | Windows.hlp |
| bmp | drawing, photography | Figure.bmp |
| jpg | Photo.jpg | |
| tif | Nature.tif | |
| gif | Figure.gif | |
| mp3 | Music | Song.mp3 |
| mpeg | video | Movie.mpeg |
| avi | clip.avi | |
| zip | ZIP archive | Abstract.zip |
| rar | WinRAR archive | Abstract.rar |
The extension can be longer than 3 characters in modern Windows, and in Linux it is not necessary at all.
In general, file extensions in Windows are often application specific, and it may be difficult or even impossible for a third-party application to open files with this extension. So, for example, the psd extension has files created in the Adobe Photoshop graphics editor (however, this program allows you to save the finished file in almost any graphic format). Text files created in Microsoft Word can be recognized by the doc extension (docx for new versions of the program), and the Open Office text editor works with the odt format. Also text files may have txt or rtf resolution.
How to find out,
What types of files does your operating system work with?
Go to Conductor, in the drop down menu Service select item Folder properties

and in the dialog box that opens, go to the tab File types.

On this tab there will be a table in two columns - the file extension in Windows and the corresponding one.
!!! Important If your computer is set up to show file extensions, then when you change the name of a file, leave the extension as it is. That is, change the file name to a dot. If you change the extension, the file may then stop opening. Remember this!
strana-sovetov.com
Main file extensions in Windows
An extension is a sequence of characters that appear after the file name (after the dot). With it, you can determine the type of data that is in this file. The extension can be written in both uppercase and lowercase letters - it doesn't matter. Usually it consists of three characters, but may consist of two.
There are files that don't have an extension at all and those that only consist of an extension. You may also come across files that have two extensions that follow each other and are separated by a dot.
The OS automatically recognizes the type of extension and launches the program for which this file is intended. Often you can't see most file extensions as they are not displayed by default. This is because there are programs installed on the computer that can easily read this extension and open the file. Accordingly, if the programs are not installed, then the extension will be indicated.
If you want the extension to always show, go to My Documents > Tools > Folder Options > View > and uncheck Hide Extensions > OK. Now you can view the file extension, both on the desktop and in File Explorer.
If you want to change it, then double-click on the file name, after it is highlighted and you can change it - change the characters after the dot to the format you need. This works in cases where Windows has inadvertently assigned the wrong format to a given . But if you want to change the MP3 or AVI format, then this file simply won't open. You can change such extensions only with the help of special programs - converters. Graphic formats are easier to change, you just need to go into the program in which they were created (for more complex formats such as PSD). This also applies to text extensions, for example, using notepad you can create web pages with an HTML or HTM extension and vice versa. Now you will get acquainted with the main types of extensions that you can see on your computer.
The main types of extensions:
ACS - a file made using the Microsoft Access program;
ARC is a file that is in the archive. To read it, you first need to unzip it. In order to view such a file, just double-click on the archive and select this file;
AU - a file that works with sound on the Internet;
AVI is a standard multimedia file found in any Windows;
CDR is a vector image created with Corel Draw;
DAT is a file that contains data;
PDF- electronic book;
DEM - the file in which the presentation is located;
DjVu is the file that stores the scanned document. DIB - a file with graphics;
DOC - text document;
DRV - driver file;
DVR - driver for any device;
EPS - image;
EXE - program;
FLR - folder;
FNT - font file;
GEM - image;
GIF(gif) - graphic file;
GRF- graphic file;
HTM - electronic page;
IMG - image;
JPG, .jpg - graphic file in JPEG format;
LZX - the file that was compressed;
MDB - database file;
MDF - menu file;
MP2 - music file;
MP3 - music file;
MPA - music file;
MPG - music file;
MRB - Windows help;
MTM - music file;
PPT - Power Point presentation;
PSD is a graphic file created with Adobe Photoshop.
RLE - compressed graphic image;
TXT - text file;
VBS - the file containing the video;
VID-driver for working with video;
XLA - add-ins in the Excel program;
XLC-chart in Excel program;
XLK - backup copy in Excel;
XLM - macro in Excel;
XLS - Excel spreadsheet;
XLT - template in Excel;
ZIP file in the archive.
As you can see, almost every file has a . If you decide to change where - either the extension - make sure that this is not a system file and not a program. Since this can lead to both the failure of the program and the system as a whole.
The extension is what helps Windows recognize and open the file, it is the most important part in the file name. You can use the extension to find out what type of data is in this file: program, video, audio, etc. Therefore, if you are unfamiliar with extensions - do not experiment by changing them, the problem may arise that it will be very difficult to restore the extension.
Subject: OS file system.
The part of the operating system that works with files is calledfile system (FS)
FS aspects(from the user's point of view) is its external representation, i.e.
naming and protecting files;
file operations;
File naming :
When a file is created, the process gives the file a name. When the process exits, the file continues to exist, and other processes can access the file by its name.
All modern operating systems 8-character text strings are used as filenames.Also, the use of numbers and special characters in file names is also allowed. Many file systems support filenames up to 255 characters.
Some file systems distinguish between upper and lower case letters (eg Unix). Under MS-DOS, there is no such distinction.
Many operating systems such asWindows 95 , Windows 98 use FSOS MS - DOS , and inherit many of its properties, including file naming.OS Windows NT , Windows 2000 also support FSMS - DOS and inherit its properties. However, the last two operating systems have their own FS( NTFS ) , which has its own properties (for example, file names in the encodingUnicode).
In many operating systems, file names can consist of 2 parts, separated by a dot
(file name. file extension) and usually means the file type.
INMS - DOS filename contains8 characters + 3 characters assigned to the file extension. On some operating systems (for example,Unix ) file extensions arejust agreements that users can stick to.
Ways to structure files:
Unstructured byte sequence.
In this caseThe OS is not interested in the contents of the file . All she sees is bytes. These bytes are assigned values by user-level programs.This approach is used in OSWindows, Unix. This approach providesmaximum flexibility .
Sequence of records
the first step to structuring files. In this model, a file is a sequence of fixed-length records, each with its own internal structure. What is important in this approach is that the read operation returns one record, and the write operation overwrites or appends one record.
The third option isthe file is a tree of records, not necessarily the same length.
Each fixed position entry contains a key field. The tree is sorted by the key field, which provides a quick search for a given key. This type of representation of file systems is widely used on large mainframes that are used for commercial data processing.
File types:
Regular files– these include all files containing user information.
Catalogs- system files that provide support for the FS structure.
Symbolic special files - are related to input-output and are used to model serial input-output devices, such as terminals, printers, networks.
Block Special Files- are used to simulate disks.
Regular files are mostly either ASCII files or binary files. ASCII files are made up of text lines. On some OSes, each line ends with carriage return character. Some (unix) use newline character. Under MS-DOS, both characters are used. The strings do not have to be the same length.
The rest of the files are called binary files, i.e. they are not ASCII files. They usually have some internal structure known to the program using them (Figure 6.2).
File access:
In older operating systems, only one access to files was provided - consistent. When accessing a file sequentially, a process can only read bytes or writes of the file sequentially.
Files whose bytes can be read in random order are called random files ( direct) access. Used for example for database applications.
File attributes:
Additional information about the file (date, time of creation) are called file attributes. The list of attributes may vary depending on the OS.
Attribute Value
Protection Who and how can access the file
Password Password to access the file
Creator ID of the user who created the file
Owner Current owner
Read-only flag 0 - for reading / writing; 1- read only
Flag "Hidden" 0 - normal, 1 - do not display in the catalog file list
Flag "System" 0 - normal; 1- systemic
Flag "Archive" 0 - archived; 1 - archiving required
ASCII Flag/Binary 0 – ASCII; 1- binary
Random access flag 0 - only sequential access; 1 - random access
Flag "temporary" 0 - normal, 1 - to delete the file at the end of the process
Block flags 0 - not blocked; non-zero for blocked
Record length Number of bytes per entry
Time of creation Date and time the file was created
Last time
access Date and time the file was last modified
current size Number of bytes in file
Maximum size Number of bytes up to which the file size can be increased
File operations
To work with files, the following system functions can be used in the OS:
Create(Creation). The file is created without data. This system call announces a new file and allows you to set some of its attributes.
Delete(deletion). Deleting a file.
open(Opening) - before working with a file, you need to open it. This system call allows the system to read the attributes of a file and a list of disk addresses into RAM for quick access to the contents of the file on subsequent calls.
close(closing).
read(reading). Reading data from a file.
Write(record). If the current position is at the end of the file, the file size is automatically increased. Otherwise, the write is made over the existing data, which is lost forever.
Append(addendum). Truncated form of Write. Can append data only to the end of the file.
Seek(Search). For random access files. Sets the file pointer to a specific position in the file. After this system call is executed, data can be read from or written to at that position.
Getattributes(getting attributes).
setattributes(Setting Attributes)
Rename(rename) - change the file name.
Filesystem types (directory form):
single level FS. Having a root directory.
Two-level directory system. The presence of a root directory - user directories.
Hierarchical (multi-level) catalog system - a set of directories and subdirectories.
System calls to work with directories:
Create - create a directory.
Delete - delete a directory.
opendir - open a directory.
Closedir Closes a directory.
Readdir Read the next entry in an open directory.
Rename - rename the directory.
Link - Establishing links.
File system structure (developer)
File systems are stored on disks. Most disks can be divided into multiple partitions with an independent filesystem on each partition.
Sector 0 of the disk is called the master boot record (MBR, MasterBootrecord) and is used to boot the computer.
At the end of the master boot record is the partition table. This table stores the start and end addresses (block numbers) of each partition. One of the partitions is marked as active in the table.
When the computer is booted, the BIOS reads and executes the MBR record, after which the bootloader determines the active disk partition in the MBR record, reads its first block, called the boot block, and executes it.
The program in the boot block loads the OS in that partition.
Every disk partition starts with a boot block, even if it doesn't contain a bootable OS.
Often FS contain some of the elements shown in Fig. 6.8. One of these elements is called superblock , contains the key parameters of the file system and is read into memory when the computer is booted or when the file system is accessed for the first time. Typical information stored in a super block includes a magic number to distinguish between system files, the number of blocks in a file system, and key administrative information.
 Next is information about free blocks file system, for example in the form bitmap or list of pointers. This information may be followed by information about i-nodes, which are an array of data structures, one structure per file, containing all the information about the files.
Next is information about free blocks file system, for example in the form bitmap or list of pointers. This information may be followed by information about i-nodes, which are an array of data structures, one structure per file, containing all the information about the files.
May be followed by root directory, containing the top of the FS tree. The rest of the space on the disk partition is occupied by all other files and directories.
FS structureMS- DOS
Hard drives are designed for permanent storage of information.
The disc has a uniform coverage in which data is stored. DOS Arranges Data in Sequences 512 bytes, which are called sectors, but in principle the operating system can organize the data on the disk as it pleases.
A file extension or file name extension is a suffix at the end of a computer file. It is usually two to four characters long. If you've ever opened a document or viewed an image, you've probably noticed these letters at the end of your file.
Screenshot of various extensions
File, what is a file, you suddenly ask? And this, in our case, is just data of a certain type stored on an electronic medium.
What is the filename extension used for?
File extensions are used by the operating system to determine which applications are associated with file types - in other words, which application opens when you double-click on a file.
For example, a file named "awesome_picture.jpg" has a "jpg" extension. For example, when you open this document in Windows, the operating system looks for any JPG-related application, opens that application, and loads the file. A extension .m4r applied
What are the types of extensions?
There are many different types There are too many file extensions to list in one article, but here are a few examples of common file extensions you may see on your computer:
DOC/DOCX: Microsoft Word document. DOC was the original extension used for Word documents, but Microsoft changed the format when Word 2007 debuted. Word Documents are now based on the XML format, so adding "X" to the end of the extension.
XLS/XLSX: - Electronic Microsoft table Excel.
PNG: Portable Network Graphics, lossless image format.
HTML/HTML: HyperText markup format for creating web pages on the Internet.
PDF: A portable document format created by Adobe and used to support formatting in distributed documents.
EXE: executable format used for programs that you can run.
And, as we said, it's just a small number of file extensions. There are literally thousands of them.
It's also important to know that there are file types that are inherently dangerous and can be dangerous. Typically, these are executable files that can run certain types of code when you try to open them.
Do not open files if they come from an untrusted source.
Under the spoiler find 50+ file extensions that are potentially dangerous for Windows
Programs
EXE- executable file programs. Most applications that run on Windows are .exe files.
PIF is a program information file for MS-DOS programs. Although .PIF files are not supposed to contain executable code, Windows will treat .PIF files the same way as .EXE files if they contain executable code.
APPLICATION - An application installer deployed using Microsoft's ClickOnce technology.
GADGET - gadget file for desktop gadget technology Windows computers, introduced in Windows Vista.
.msi file Microsoft installations. They install other applications on your computer, although applications can also be installed by .exe files.
MSP - Patch File Windows Installer. Used to patch applications deployed in .MSI files.
COM - The original program type used by MS-DOS.
SCR - Windows Screen Saver. Windows screensavers may contain executable code.
HTA is an HTML application. Unlike HTML applications that run in browsers, .HTA files run as robust applications without a sandbox.
CPL - Control Panel File. All utilities found in the panel Windows controls, are .CPL files.
MSC - Microsoft Management Console file. Applications such as editor group policy and Disk Management are .MSC files.
JAR - .JAR files contain executable Java code. If you have the Java Runtime Environment installed, .JAR files will run as programs.
Scenarios
BAT is a batch file. Contains a list of commands that will run on your computer if you open it. Originally used MS-DOS.
CMD is a batch file. Similar to .BAT, but this file extension was introduced in Windows NT.
VB, .VBS - VBScript file. Executes its included VBScript code if you run it.
VBE - Encrypted VBScript file. Similar to a VBScript file, but it's not easy to determine what the file will do if you run it.
js - JavaScript file. .JS are commonly used by web pages and are safe when run in web browsers. However, Windows will run .JS files outside of a non-sandboxed browser.
JSE - Encrypted JavaScript file.
WS , .WSF - Windows script file.
WSC, .WSH - Windows Script and Windows Script Host script files. Used in conjunction with Windows script files.
PS1 , .PS1XML , .PS2 , .PS2XML , .PSC1 , .PSC2 - Windows PowerShell script. Performs PowerShell commands in the order specified in the file.
MSH , .MSH1 , .MSH2 , .MSHXML , .MSH1XML , .MSH2XML - Monad script file. The monad was later renamed to PowerShell.
Labels
SCF - Batch File windows explorer. Can pass potentially dangerous commands to Windows Explorer.
INF is a text file used by AutoRun. If run, this file could potentially launch dangerous applications that it comes with or pass dangerous options to programs included with Windows.
Others.REG - File Windows Registry. .REG files contain a list of registry entries that will be added or removed if you run them. A malicious .REG file can remove important information from your registry, replace it with unwanted data, or add malicious data.
Office Macros
DOC, .XLS, .PPT - Microsoft documents Word, Excel and PowerPoint. They may contain malicious code macro.
DOCM , .DOTM , .XLSM , .XLTM , .XLAM , .PPTM , .POTM , .PPAM , .PPSM , .SLDM. New file extensions introduced in Office 2007. The M at the end of a file extension indicates that a document contains macros. For example, a .DOCX file does not contain macros, but a .DOCM file can contain macros.
This is not an exhaustive list. There are other types of file extensions - such as .PDF - that have a number of security issues. However, for most file types above, there are none. They exist to run arbitrary code or commands on your computer.
What should I do if I don't see file extensions on my computer?
By default, Windows shows file extensions. For a while - in Windows 7, 8 and even 10 - this was not true, but luckily they changed the default settings.
We say that showing file extensions is not only useful, but also safer. Without showing extensions, it's hard to tell if the PDF you're viewing (for example) is really PDF file, not some malicious executable plot.
If file extensions don't show up in Windows, it's easy enough to get that information back. From any file explorer window, simply select View ⯮ Options ⯮ Change Folder and search options.

screenshot of how to control the visibility of file extensions in Windows
In the Folder Options window, on the View tab, select the Hide extensions for known file types check box.
On macOS, file extensions are not displayed by default. The reason for this is that macOS doesn't really use extensions the way Windows does (which we'll talk more about in the next section).
However, you can do macOS file extensions and that's probably not too bad. With Finder open, simply go to Finder⯮ Preferences⯮ Advanced and then check the "Show all file extensions" box.

How do macOS and Linux use file extensions?
So we've talked about how Windows uses file extensions to find out what type of files it's dealing with and what application to use when opening a file.
Windows knows that the file named readme.txt is text file because of this .txt file extension and it knows how to open it with the default text editor. Remove this extension and Windows will no longer know what to do with the file.
While MacOS and Linux still use file extensions, they don't rely on them like Windows does. Instead, they use something like MIME and creator codes to determine what the file is. This information is stored in the header of the file, and both macOS and Linux use this information to determine what type of files they are dealing with.
Since file extensions are not really required on macOS or Linux, you could very well have a valid file without the extension, but the OS can still open the file with the correct program due to the file information contained in the file's header.
What happens if I change the file extension?
Based on what we just talked about in the previous section, what happens when you change your file extension depends on which operating system you're using.
On Windows, if you remove a file extension, that operating system no longer knows what to do with that file. When you try to open the file, Windows will ask you which application you want to use. If you change the extension say you renamed the file from "coolpic.jpg" to "coolpic.txt" -Windows will try to open the file in the application associated with the new extension and you will get an error or an open but useless file.
In this example, Notepad (or any other default text editor) opened our "coolpic.txt" file, but it's just garbled jumbled text.

By this cause Windows warns you when you are trying to change the file extension and you must confirm the action.

If you're using macOS, something similar happens. If you try to change the file extension, you will receive a warning.

If you change the extension to something else, macOS will try to open the file in the app associated with the new extension. And you will get an error message or a malformed file - just like in Windows.
Unlike Windows, if you try to remove a file extension in macOS (at least in Finder), macOS simply appends the same extension back using the data from the file's MIME type.
If you really want to change the file type - for example you would like to change an image from JPG to PNG format - you will need to use software, which can actually convert the file.
How to change the program that opens a file
Whenever you install an application that can open a specific type of file, that application and file extension are registered with your operating system. It is possible that multiple applications may open the same file.
You can launch the application and then upload any supported file type to it. Or you can right click the file to open it context menu and select an available application there.
For example, in the image below, you can see that we have several image apps in our Windows system which can open the "coolpic.jpg" file that we right-clicked.

However, there is also a default application associated with each extension. This app opens when you double-click on a file, and on Windows, it's the app that appears at the top of the list you get when you right-click on a file (pictured above).
And you can change this default application. Just go to Settings ⯮ Applications ⯮ Default apps ⯮ Select default apps by file type. Scroll through the (very long) list of file types to find the one you want, then click its associated application on the right to change it.

And you can do the same on macOS. Just select the file of the type you want to change and choose File > Get Info from the main menu. In the Info window that appears, navigate to the "Open With" section, and then select your new application from the drop-down menu. Easy enough.

Now you know what a file extension is and how to change it.
There are many types of files. They can be text, graphics, music, software, etc. To make it easier for both the user and the operating system to navigate in such a variety, each file has its own extension, which is a kind of identifier. The following guide will help you understand why you need to know the file extension, how to enable the display of such information in the Windows operating system, and how you can determine the format of a file that does not have a visible extension.
Sometimes the user's computer in one way or another gets files with which his operating system did not have to work before. Most likely, the program required to interact with such files will not be installed either. The system notifies you of this with the following message:

It provides information about the file name, as well as a standard message notifying that the operating system does not know what programs support working with this extension. The user has 2 options for further actions:
- Find a suitable program on the Internet.
- Select the required application yourself from the list of installed ones.
Practice shows that the first option is useless - usually nothing sensible can be found. But the second solution is very effective. Knowing the file extension, you can easily find a suitable program using the capabilities of your favorite search engine.
How to enable display of extensions
By default, the display of extensions in the Windows operating system is disabled. Experienced users, if necessary, can activate this function on their own, while inexperienced users do not need it - they can accidentally change the extension of an important system file, which will lead to various violations of Windows.
If you need to enable the display of extensions, you probably know why you are doing this. In such a situation, follow the instructions below.

How to find file format without extension
Even after turning on the display of the extension, some files will be shown without it. An example can be seen in the following screenshot.

The landing page looks like this.