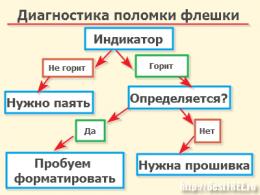
Lesson general principles of building LAN local networks. Coursework: Designing a local area network Creating a local
Building a local network
In this article, we will talk about the local network. It's no secret that local network installation on any site is a vital necessity for business. Data exchange between computers, Internet access, IPtelephony, access to network printers and a server, the company makes the installation of a local network a must for any company.
In small local networks, all computers are usually equal, i.e. users themselves choose which resources of their personal computer to make publicly available. Such networks are called peer-to-peer local networks. Thus, the user of a peer-to-peer local network chooses which folders, files to share and make available to other computers on the local network.
A more complex local network involves installing a server in it. If there are a large number of computers in the local network to increase its performance, as well as to increase the reliability of storing information on the local network, separate computers are allocated for storing data or application programs. A server machine differs from a conventional computer in higher performance, storage array and fault tolerance. The network in which the server is present is commonly referred to as a server-based LAN.
In such a local network, the server can perform different tasks:
- Shared LAN database
- connection of peripheral devices
- centralized management of the local network
- message routing definitions
Building a local network
Consider an example of building a peer-to-peer local network. Such a local network will consist of a modem, router, access point, hub and cable route. The installation of a local network begins with the receipt of a technical specification from the customer: network capacity, location of points, method of laying cable routes, a room allocated for a server room or an installation site for active equipment. Installation of a 100 megabit LAN is usually carried out with a UTP network cable of at least 5 AWG24 category (4 pairs, 0.5 mm cross section of one core). If the route for mounting the local network passes near power cables or other sources of electromagnetic interference, it is better to use an FTP cable. FTP network cable differs from UTP network cable by having a steel wire shield. Thus FTP has the best performance noise immunity, provided that at the end the cable is crimped with a metallized connector with the cable screen embedded under the connector and the computer has a ground loop. The total cable length of the line from the computer to the hub, in theory, should not exceed 100m, but in practice, depending on the cable and the influence of electro-magnetic components, it can reach up to 160m, but from 100Mbps it remains about 4-7 Mbps. To build gigabit networks, a cable, connectors and patch panels of the 6th category are used. In the server room or the place where the active equipment is installed network cable crimped with RJ45 connectors or crossed to a patch panel and connected to a hub. On the other side, a network outlet is placed, to which the computer is connected. From the requirements for personal computer: It must have a network adapter. A router is connected to the hub, which, as often happens, is combined with a modem and an access point. Installation of a wireless access point can be done separately, depending on the required coverage area. Setting up such a local network should not cause any difficulties. In a simple variant, computers are located on the same subnet and access the router to access the Internet. The access point also talks to the router for Internet access. Thus, we have built a peer-to-peer network for a small company.
A larger local network will not do without installing a server. Installation of cabling also begins with the terms of reference as discussed above for a peer-to-peer local network. The terms of reference should also be formed at the logical level: requirements for the server, software: database, ftp -server, Internet server, print server, security policy implementation. Typically, these requirements are imposed on the administrator serving the local network of an organization or a company that, together with the installation, configures the local network. In such a network, you can install a switch of a higher level, with gigabit ports for connecting to a server gigabit adapter. For example, in such a network, access to the Internet will already be carried out through a server on which software is installed to provide access and monitor the activities of personnel on the Internet. Each computer can have its own access rights defined by the security policy of the server in the domain. Each computer for authorization in the domain must enter the name and password issued by the network administrator

At the end, let's summarize:
The first peer-to-peer network we reviewed is widely used in small offices and homes with up to 10 computers. Active equipment is inexpensive and easy to set up. Users of such a network can independently configure the security policy in relation to their computer, share individual files and folders. Maintenance by a network administrator is not required.
Large local networks, which are subject to high requirements for security, performance and other functionality, cannot do without server machines. Such a local area network is difficult to set up, and the cost of active equipment increases significantly due to the server(s). The performance of such a network is much higher, the computer user is limited in rights by the general security policy of the domain. The server provides various services to user machines depending on access levels: access to the Internet, to network printers, to ftp -resources, to mail, to a common database, etc. It is desirable to have an employee to maintain such a network. In a large distributed local area network of an enterprise, there may be several servers, each of which will perform its task: Internet server, ftp -server, print server, database server, server used for low voltage: collection of reports from mini PBX, server of integrated security systems for video surveillance, access control, fire alarm.
Safe Kuban performs installation and maintenance of local wired and wireless systems in Krasnodar and in the South of Russia
By itself, the concept of a local network means combining several computers or computer devices into a single system for exchanging information between them, as well as sharing their computing resources and peripheral equipment. Thus, local networks allow:
Exchange data (movies, music, programs, games, etc.) between network members. At the same time, to watch movies or listen to music, it is absolutely not necessary to record them on your own. HDD. The speeds of modern networks allow you to do this directly from remote computer or multimedia device.
Connect simultaneously several devices to the global Internet through one access channel. This is probably one of the most requested features of local area networks, because today the list of equipment that can use a connection to the World Wide Web is very large. In addition to all possible computer technology and mobile devices, TVs, DVD/Blu-Ray players, multimedia players and even all sorts of Appliances ranging from refrigerators to coffee makers.
Share computer periphery equipment such as printers, MFPs, scanners, and network storages data (NAS).
Share the computing power of computers of network participants. When working with programs that require complex calculations, such as 3D visualization, to increase performance and speed up data processing, you can use the free resources of other computers on the network. Thus, having several weak machines connected to a local network, you can use their total performance to perform resource-intensive tasks.
As you can see, creating a local network, even within the same apartment, can bring a lot of benefits. Moreover, the presence of several devices at once at home that require an Internet connection is not uncommon for a long time, and combining them into a common network is an urgent task for most users.
Basic principles of building a local network
Most often, local networks use two main types of data transfer between computers - by wire, such networks are called cable networks and use Ethernet technology, as well as using a radio signal over wireless networks built on the basis of the IEEE 802.11 standard, which is better known to users under the name Wi -Fi.
To date, wired networks still provide the highest throughput, allowing users to exchange information at speeds up to 100 Mbps (12 Mbps) or up to 1 Gbps (128 Mbps) depending on the equipment used (Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet). And although modern wireless technologies theoretically can also provide data transfer up to 1.3 Gb / s (Wi-Fi 802.11ac standard), in practice this figure looks much more modest and in most cases does not exceed 150 - 300 Mb / s. The reason for this is the high cost of high-speed Wi-Fi equipment and the low level of its use in current mobile devices.
As a rule, everything modern networks are arranged according to the same principle: user computers (workstations) equipped with network adapters are connected to each other through special switching devices, which can be: routers (routers), switches (hubs or switches), access points or modems. We will talk in more detail about their differences and purposes below, but for now just know that without these electronic boxes, it will not work to combine several computers at once into one system. The maximum that can be achieved is to create a mini-network of two PCs by connecting them to each other.
We must not forget that the local network is a "product" with individual solutions for each specific case, which does not tolerate an ill-conceived approach. That is why, like any quality product, a local network must be built by professionals. Let's take a look at what we need to know in order to conduct a quality installation.
At the very beginning, you need to determine the basic requirements for your future network and its scale. After all, the number of devices, their physical placement and possible ways connection, the choice of the necessary equipment will directly depend.  Most often, a home local area network is combined and it can include several types of switching devices at once. For example, desktop computers can be connected to the network via wires, and various mobile devices (laptops, tablets, smartphones) via Wi-Fi.
Most often, a home local area network is combined and it can include several types of switching devices at once. For example, desktop computers can be connected to the network via wires, and various mobile devices (laptops, tablets, smartphones) via Wi-Fi.
For example, consider one of the options home local network. It will involve electronic devices designed for various purposes and tasks, as well as using different type connections.
As can be seen from the figure, several desktop computers, laptops, smartphones, set-top boxes (IPTV), tablets and media players and other devices can be combined into a single network at once. Now let's figure out what kind of equipment you need to build your own network.
Network Card

A network card is a device that allows computers to communicate with each other and exchange data on a network. All network adapters by type can be divided into two large groups - wired and wireless.
Wired network cards allow you to connect electronic devices to a network using Ethernet technology using a cable, and wireless network adapters use Wi-Fi radio technology.
As a rule, all modern desktop computers are already equipped with Ethernet network cards built into the motherboard, and all mobile devices (smartphones, tablets) are equipped with Wi-Fi network adapters.  At the same time, laptops and ultrabooks are mostly equipped with both network interfaces at once.
At the same time, laptops and ultrabooks are mostly equipped with both network interfaces at once.
Despite the fact that in the vast majority of cases, computer devices have built-in network interfaces, sometimes it becomes necessary to purchase additional boards, for example,  to equip the system unit wireless module WiFi connections.
to equip the system unit wireless module WiFi connections.
According to their constructive implementation, individual network cards are divided into two groups - internal and external. Internal cards designed for installation in desktop computers using interfaces and their corresponding PCI and PCIe slots. External boards are connected via USB connectors or outdated PCMCIA (laptops only).
Router (Router)

The main and most important component of a home local network is a router or router - a special box that allows you to combine several electronic devices into a single network and connect them to the Internet through a single channel provided to you by your ISP.
A router is a multifunctional device or even a minicomputer with its own embedded operating system that has at least two network interfaces. The first of them - LAN (Local Area Network) or LAN (Local Area Network) is used to create an internal (home) network, which consists of your computer devices. The second - WAN (Wide Area Network) or WAN (Global Computing Network) is used to connect a local area network (LAN) to other networks and the World Wide Web - the Internet.
The main purpose of devices of this type is to determine the paths (routing) of data packets that the user sends to other, larger networks or requests from them. It is with the help of routers that huge networks are divided into many logical segments (subnets), one of which is the home LAN. Thus, at home, the main function of the router can be called the organization of the transfer of information from the local network to the global network, and vice versa.
Another important task of the router is to restrict access to your home network from world wide web. Surely you are unlikely to be satisfied if anyone can connect to your computers and take or delete from them whatever they want.
To prevent this from happening, the data flow intended for devices belonging to a specific subnet must not go beyond its limits. Therefore, the router from the total internal traffic generated by the members of the local network selects and sends to the global network only that information that is intended for other external subnets. This ensures the security of internal data and saves overall throughput networks.
The main mechanism that allows the router to restrict or prevent access from common network(outside) to devices on your local network is called NAT (Network Address Translation). It also provides all users of the home network with access to the Internet by converting several internal addresses of devices into one public external address provided by your Internet service provider. All this makes it possible for computers on the home network to easily exchange information with each other and receive it from other networks. At the same time, the data stored in them remains inaccessible to external users, although at any time access to them can be provided at your request.
In general, routers can be divided into two large groups - wired and wireless. Already by the names it is clear that all devices are connected to the first ones only with the help of cables, and to the second ones, both with the help of wires and without them using Wi-Fi technology. Therefore, at home, it is wireless routers that are most often used, which allow providing Internet and networking computer equipment using various communication technologies.

To connect computer devices using cables, the router has special sockets called ports. In most cases, the router has four LAN ports for connecting your devices and one WAN port for connecting an ISP cable.
In many cases, the router may be the only component needed to build your own local network, as there will simply be no need for the rest. As we have already said, even the simplest router allows you to connect up to four computer devices using wires. Well, the number of equipment that receives simultaneous access to the network using Wi-Fi technology can even be in the tens, or even hundreds.
If, nevertheless, at some point the number of LAN ports of the router is no longer enough, then to expand the cable network, one or more switches can be connected to the router (we will discuss them below), which act as splitters.
Modem
In modern computer networks, a modem is a device that provides access to the Internet or access to other networks through ordinary wired telephone lines (xDSL class) or using wireless mobile technologies(class 3G).
 Conventionally, modems can be divided into two groups. The first includes those that connect to the computer through USB interface and provide access to the network only one specific PC, to which the modem is directly connected. In the second group, LAN and / or Wi-Fi interfaces already familiar to us are used to connect to a computer. Their presence indicates that the modem has a built-in router. Such devices are often called combined, and they should be used to build a local network.
Conventionally, modems can be divided into two groups. The first includes those that connect to the computer through USB interface and provide access to the network only one specific PC, to which the modem is directly connected. In the second group, LAN and / or Wi-Fi interfaces already familiar to us are used to connect to a computer. Their presence indicates that the modem has a built-in router. Such devices are often called combined, and they should be used to build a local network.

When choosing DSL equipment, users may encounter certain difficulties caused by confusion in its names. The fact is that often in the assortment of computer stores, two very similar classes of devices coexist at once: modems with built-in routers and routers with built-in modems. What is their difference?
There are practically no key differences between these two groups of devices. Manufacturers themselves position a router with a built-in modem as a more advanced option, endowed with a large number of additional features and improved performance. But if you are only interested in basic features, such as connecting all computers on a home network to the Internet, then there is not much difference between modem routers and routers where a DSL modem is used as an external network interface.
So, to summarize, a modern modem with which you can build a local network is, in fact, a router with an xDSL or 3G modem acting as an external network interface.
Switch
A switch or switch is used to connect various nodes of a computer network and exchange data between them via cables.
The role of these nodes can be either separate devices, such as a desktop PC, or entire groups of devices already combined into an independent network segment. Unlike a router, the switch has only one network interface - LAN and is used at home as an auxiliary device, mainly for scaling local networks.

To connect computers using wires, like routers, switches also have special socket-ports. In models focused on home use, usually their number is five or eight. If at some point the number of switch ports is no longer enough to connect all devices, you can connect another switch to it. Thus, you can expand your home network as much as you like.
Switches are divided into two groups: managed and unmanaged. The first, as the name implies, can be controlled from the network using special software. With advanced functionality, they are expensive and not used in the home. Unmanaged switches distribute traffic and regulate the speed of data exchange between all network clients in automatic mode. It is these devices that are ideal solutions for building small and medium-sized local networks, where the number of participants in the exchange of information is small.
Depending on the model, the switches can provide a maximum data transfer rate of either 100 Mbps (Fast Ethernet) or 1000 Mbps (Gigabit Ethernet). Gigabit switches are best used for building home networks in which it is planned to frequently transfer large files between local devices.
Wireless access point
To provide wireless access to the Internet or local network resources, in addition to a wireless router, you can use another device called wireless hotspot access.
Unlike a router, this station does not have an external WAN network interface and is equipped in most cases with only one LAN port for connecting to a router or switch. Thus, you will need an access point if your local network uses a regular router or modem without Wi-Fi support.

The use of additional access points in a network with a wireless router can be justified in cases where a large Wi-Fi coverage area is required. For example, the signal strength of a wireless router alone may not be enough to cover the entire area in a large office or a multi-storey country house.
Access points can also be used for organizing wireless bridges, allowing you to connect individual devices, network segments or entire networks using a radio signal in places where cabling is undesirable or difficult.
Network cable, connectors, sockets
Despite the rapid development of wireless technologies, many local networks are still built using wires. Such systems have high reliability, excellent throughput and minimize the possibility of unauthorized connections to your network from outside.

To create a wired local area network in home and office conditions, Ethernet technology is used, where the signal is transmitted over the so-called “twisted pair” (TP-Twisted Pair) - a cable consisting of four copper twisted pairs of wires with each other (to reduce interference).
When building computer networks, mostly unshielded CAT5 cable is used, and more often its improved version CAT5e. Cables of this category allow you to transmit a signal at a speed of 100 Mbps when using only two pairs (half) of wires, and 1000 Mbps when using all four pairs.

To connect to devices (routers, switches, network cards, and so on) at the ends of a twisted pair, 8-pin modular connectors are used, commonly referred to as RJ-45 (although they correct name— 8P8C).
Depending on your desire, you can either buy ready-made (with crimped connectors) network cables of a certain length, called “patch cords”, in any computer store, or purchase them separately twisted pair and connectors, and then independently make cables of the required size in the right quantity.
Using cables to connect computers to a network, of course, you can connect them directly from switches or routers to connectors on PC network cards, but there is another option - using network sockets.
In this case, one end of the cable is connected to the switch port, and the other to the internal contacts of the socket, in the external connector of which you can later connect computer or network devices.

Power outlets can be built into the wall or mounted outside. The use of sockets instead of protruding cable ends will give a more aesthetic look to your workplace. It is also convenient to use sockets as reference points for various network segments. For example, you can install a switch or router in the hallway of the apartment, and then thoroughly lay cables from it to sockets located in all necessary rooms. Thus, you will get several points located in different parts of the apartment, to which you can connect not only computers, but also any network devices at any time, for example, additional switches to expand your home or office network.
Another little thing that you may need when building a cable network is an extension cable, which can be used to connect two twisted pairs with already crimped RJ-45 connectors.
In addition to their direct purpose, extension cords are convenient to use in cases where the end of the cable ends with not one connector, but two. This option is possible when building networks with a bandwidth of 100 Mbps, where only two pairs of wires are sufficient for signal transmission.
 You can also use a network splitter to connect two computers to one cable at once without using a switch. But again, it is worth remembering that in this case the maximum data exchange rate will be limited to 100 Mbps.
You can also use a network splitter to connect two computers to one cable at once without using a switch. But again, it is worth remembering that in this case the maximum data exchange rate will be limited to 100 Mbps.
Read more about twisted pair crimping, connecting sockets and the characteristics of network cables in a special material.
Network topology
Now that we've seen the basic components of a LAN, it's time to talk about topology. If to speak plain language, then network topology is a diagram that describes the locations and methods of connecting network devices.
There are three main types of network topology: Bus, Ring, and Star. With a bus topology, all computers on the network are connected to one common cable. To combine PCs into a single network using the "Ring" topology, they are serial connection with each other, with the last computer connected to the first. With a star topology, each device is connected to the network through a special hub using a separate cable.
Probably, the attentive reader has already guessed that to build a home or small office network, the Star topology is mainly used, where routers and switches are used as hub devices.
Creating a network using the Zvezda topology does not require deep technical knowledge and large financial investments. For example, using a switch that costs 250 rubles, you can network 5 computers in a few minutes, and using a router for a couple of thousand rubles, you can even build a home network, providing several dozen devices with access to the Internet and local resources.
Another undoubted advantage of this topology is good scalability and ease of upgrade. Thus, network branching and scaling is achieved by simply adding additional hubs with the necessary functionality. Also, at any time, you can change the physical location of network devices or swap them in order to achieve more practical use of equipment and reduce the number and length of connecting wires.
Despite the fact that the Zvezda topology allows you to quickly change the network structure, the location of the router, switches and other necessary elements must be thought out in advance, in accordance with the layout of the room, the number of connected devices and how they are connected to the network. This will minimize the risks associated with the purchase of unsuitable or redundant equipment and optimize the amount of your financial costs.
Conclusion
In this article, we reviewed general principles building local networks, the main equipment that is used and its purpose. Now you know that the main element of almost any home network is a router, which allows you to network many devices using both wired (Ethernet) and wireless (Wi-Fi) technologies, while providing all of them with an Internet connection through one single channel.
Switches are used as ancillary equipment to expand the points of connection to the local network using cables, which are essentially splitters. To organize wireless connections, access points are used, which allow using Wi-Fi technology not only to connect all kinds of devices wirelessly to the network, but also in the "bridge" mode to connect entire segments of the local network.
In order to understand exactly how much and what kind of equipment you will need to purchase to create a future home network, be sure to first draw up its topology. Draw a diagram of the location of all devices participating in the network that will need to cable connection. Depending on this, select the optimal location for the router and, if necessary, additional switches. There are no uniform rules here, since physical location router and switches depends on many factors: the number and type of devices, as well as the tasks that will be assigned to them; the layout and size of the room; requirements for the aesthetics of the type of switching nodes; possibilities for laying cables and others.
So, as soon as you have a detailed plan for your future network, you can begin to move on to the selection and purchase of the necessary equipment, its installation and configuration. But we will talk about these topics in our next materials.
Let's decide on the starting points: a small company, let's say about 15-50 employees. As a rule, there is no qualified network specialist. And most likely it was the "dedicated" for working with the network, the network administrator by state. Let's agree - your specialist is still needed. And he needs to be paid money, and good money at that (what a horror, right? That's news for many directors). I will try in this article (perhaps with a continuation) to act as a network administrator for such a small company. So, we build a network ourselves. Why not? There are many arguments "against" "home-made", and all of them are true (unless, of course, this is not outright "noodles" from a potential contractor). But still, you can do it yourself. Arguments "for" also abound. We will not bring them here - we believe that we decided to do it ourselves. We will not make new-fangled radio, Wi-Fi and other networks, but an inexpensive, but high-quality cable network of a traditional wired type for the daily work of the company. However, one must understand that the work must be performed by a specialist (or several).
Introduction
Let's decide on the starting points: a small company, let's say about 15-50 employees. As a rule, there is no qualified network specialist. And most likely it was the "dedicated" for working with the network, the network administrator by state. If there is - a jack of all trades, and often forced to deal with some "urgent" business like Windows installation or drivers on some computer, instead of working with the network. Together with other "computers" (if any). Is the network working? Let the deck through the stump, well, okay, a little later we will do it (let's do it).
Let's agree - your specialist is still needed. And he needs to be paid money, and good money at that (what a horror, right? That's news for many directors). I will try in this article (perhaps with a continuation) to act as a network administrator for such a small company.
Initial data
So, we build a network ourselves. Why not? There are many arguments "against" "home-made", and all of them are true (unless, of course, this is not outright "noodles" from a potential contractor). But still, you can do it yourself. Arguments "for" also abound. We will not bring them here - we believe that we decided to do it ourselves.However, one must understand that the work must be performed by a specialist (or several). You can’t train (“though inferior, but your own”) and raise your specialist in this way. You can put your own into practice to the person doing the work (we will not take into account drilling holes with a puncher in the walls and fixing the cable channel - any man should be able to do this).
One more factor, let's add, so to speak, "pepper" - our company, in addition to the office, has a store and a warehouse, which are quite remote.
We will not make new-fangled radio, Wi-Fi and other networks, but an inexpensive, but high-quality cable network of a traditional wired type for the daily work of the company. For work, not for surfing news and/or porn sites from a laptop from a hotel couch. We may return to these issues in the sequel (not to the hotel and others like it, of course, but to modern technologies).
Last, and also very important: we count money, but we are not greedy.
Plan
At the very beginning, you must definitely do one very simple, but very important thing - take a few pieces of paper, a pencil and sit down for a draft business plan. It is very important to more or less clearly "take on a pencil" everything keywords, which will come to mind from the question "what do I want from the network." Sketch these positions on the first sheet. On the second - to group them into separate categories. For example - the category "services". What kind of services do we want to receive from the network, and what quality? What do we need? File-, ftp-, print-, internet service?It would seem that everything is clear, why write, draw? But, if you do not take everything on a pencil - then it will be worse. For example, it turns out that you need to go to the director and / or to the accounting department: “Sorry, we bought the wrong piece of iron here, and not for 100 USD. necessary, but for 500.
Now you can take a break to add what you need, throw away the excesses. And put it all aside for at least a day. Then the draft can be transferred to the third sheet. With "final" additions and corrections. Why quotes - you yourself understand, this is not the last sheet, and far from the last "sketches".
Services are services, however, the base is SCS, that is, a structured cabling system. Let's try not to run too far ahead of the horse.
Usually there are two options - an office "from scratch" and an office "ready". The first case - bare walls and ceiling, repair - ours, and that's good. The second option is "done". Those. - we begin the external laying of the SCS. But, let's not start with that, yet.
Electricity
An important stage, because God forbid, not just one or two ordinary computers “fly”, everything can “fly”. Well, we believe that everything is in order with the power network in our office. There is only one important point here - uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). They are necessary. Believe me. A diesel generator is, of course, good, but not necessary in all cases, but sparing money on installing a UPS on each server or communication closet is simply stupid. However, we will return to the issue of UPS in due time.SCS and basic active equipment
Structured Cabling System (SCS) is one of the cornerstones. SCS must be properly designed and built. Let's break the question into sections:
* Communication cabinet (with "stuffing")
* Cable lines
* Subscriber sockets
This is where the plan of the premises, with clearly marked places for employees, is very useful. It must be borne in mind - it’s also good to note power sockets. Next - in order, let's start with the closet.
Communication cabinet: find a convenient place to install a cabinet with equipment. It is important to find the optimal distance to workstations in order to reduce the cost of twisted pair, cable channel and other "little things". There are many factors: limiting the length of the line to 100 meters (or rather, 90 meters, according to the classical formula 90 + 5 + 5); office layout (where is it convenient to put or hang a cabinet, is it convenient to pass the walls when pulling the cable, will the cooling not put pressure on the ears of customers or employees, etc.); in fact, the design of the cabinet (floor, wall, its height in U, the amount of equipment that needs to be installed in it, whether there will be a cooling unit).
There are a wide variety of cabinets, you need to carefully look at the prices and quality of the proposed purchase, do not forget to stock up on capacity (!) In those very U. Be sure to have at least one shelf. However, in some places it is quite possible to get by with wall brackets to secure equipment. But this is specificity. We will assume that for the office we chose a 12-14-height cabinet with a glass door. Looking ahead a little, it is necessary to mention what will be installed inside:
Shelf: it will always come in handy, even if it is empty (I doubt it) - it can be removed. You should not spare 10-20 dollars when you have to "suddenly" put a device or two in the closet, remember these lines.
Switch (switch): 24 ports at the lower limit of the company's employees in the office - let there be 10-20 people in the office (and do not forget about servers and other network equipment). However, if there is a high density of jobs, there will be no problems adding the required number of switches and other related equipment.
Distribution panel (patch panel): 24 ports, everything is the same with the switch. It is on the patch panel that all lines from workstations and servers will be reduced.
Panel (block) of power sockets: by the number of connected equipment in the cabinet, plus a supply of 1-2 sockets on the panel. Here we may well expect an "ambush" if we have to connect power supplies - it may not be enough (remember 99.9% of the market filled with surge protectors with tightly-obliquely planted sockets).
You can put a cheap, simple option (that's when a shelf comes in handy, but you can also put it on the floor of a cabinet), you can also use a 19 ”UPS designed for installation in a cabinet.

So, having looked at the products offered on the market, we believe that we have decided on a cabinet: 14-height (14 U). For example, Molex MODBOX II 14U:
Suitable for 19" 1U fan cabinet
. Standard cabinet set:
. Lightweight steel profile provides the cabinet with greater rigidity and strength
. Aesthetic glass door with lock
. Door of universal design with the possibility of hanging (left, right)
. 19" depth adjustable frame
. Grounding of all cabinet elements
. The cable entry holes are equipped with a protective brush to prevent dust from entering the cabinet
Switch. His choice is a more complex issue. Absolutely cheap switches do not want to be considered. There are devices that are more expensive (and very expensive), but you still have to choose from two types: unmanaged and managed.
Let's take a look at the following two devices: ZyXEL Dimension ES-1024 and ES-2024:

It is a cost-effective Fast Ethernet solution and can be used to build highly efficient switched networks. The data staging feature significantly reduces latency on high-speed networks. The switch is designed for workgroups, departments or backbones. computing environments for small and medium enterprises. Due to the large address table and high performance, the switch is an excellent solution for connecting departmental networks to a corporate backbone or for connecting network segments.
Specifications:
24-port Fast Ethernet switch
. IEEE 802.3, 802.3u and 802.3x compliant
. RJ-45 Ethernet ports with 10/100 Mbps auto-speed selection
. Automatic crossover cable connection detection on all 10/100 Mbps RJ-45 Ethernet ports
. Back-Pressure-Base flow control support on half-duplex ports
. Pause-Frame-Base flow control support on full duplex ports
. Store-and-forward switching support
. Support for automatic address detection
. Max Speed wired network transfers
. Built-in MAC address table (8K MAC address capacity)
. Power LEDs, LK/ACT and FD/COL

Application of ES-2024 Switch will allow you to unite a group of users and connect them with high-speed lines to the corporate network. Additionally, it will be possible, thanks to the use of iStackingTM technology, to combine a group of switches for network management, regardless of their location.
Specifications:
24 RJ-45 ports with 10/100 Ethernet auto-speed selection and auto-sensing crossover cable connection
. 2 x 10/100/1000 Ethernet ports
. 2 mini-GBIC standard slots, combined with ports
. 8.8 Gbps non-blocking switching bus
. Support for IEEE 802.3u, 802.3ab, 802.3z, 802.3x, 802.1D, 802.1w, 802.1p protocols
. MAC address table 10Kb
. VLAN support: Port-based and 802.1Q
. Possibility to limit the rate on the port
. 64 static VLANs and up to 2Kb dynamic VLANs
. MAC address filtering
. Support for ZyXEL iStacking™, up to 8 switches (up to 24 in the future) managed by a single IP address
. Control via RS-232 and WEB-interface
. Telnet CLI
. SNMP V2c(RFC 1213, 1493, 1643, 1757, 2647)
. Control over IP: static IP or DHCP client
. Firmware update via FTP
. Updating and Saving System Configuration
. Standard 19" Rack Mount
As you can see, there is a difference, and a very significant one. As there is a difference in price - approximately 100 and 450 dollars. But, if the first switch is a decent, but "stupid" box, then the second one is in some sense intelligent, with much more functionality and manageable, with potentially strengths. We choose the second option. We want to build a good network, don't we?
By the way, right now it is quite time to ask yourself why, in fact, we are building a “hundredth” network? Today, every second computer has not just a gigabit network interface, but two gigabit ones?
This is the case where you can safely save. The fact is that a 100-megabit network is more than enough for an office to work. If, moreover, the switch is decent! Yes, but on the two gigabit interfaces of the selected switch - safely "sit down", for example, two servers. Here they are, the servers, it's just for the benefit.
Of course, you can take something like a ZyXEL GS-2024 and put everyone on a gigabit channel, but this is just a case of unreasonable spending of money, and for that kind of money we can buy a complete cabinet with a more complete filling.

Patch panel. Also the case when you should not save much. Choose a panel like Molex 19" 24xRJ45, KATT, 568B, UTP, PowerCat 5e, 1U.
Compliance with the requirements of category 5e. The compensation system is implemented directly on the printed circuit board. The use of CATT type connectors speeds up and simplifies cable installation. Dedicated space for labeling channels. The panel is powder coated. All necessary fastening and marking elements are supplied in the kit.
There are many options here, as already mentioned, you can put any cheap one, it can be more expensive, you can use a 19” rack-version - there will be beauty at all. Who doesn't know APC? You can see for example this UPS:

APC Smart-UPS SC 1500VA 230V - 2U Rackmount/Tower
Or, like this:

Without delving into the characteristics, we note that many devices are equipped on request with guides for installing the UPS in a 19 "rack. Also, it is possible to equip, if desired, with an SNMP module for monitoring and managing the UPS over a computer network. Of course, this will cost money, but It can be very convenient.Let's opt for IPPON.It should be noted that models 1500, 2000 and 3000 can be equipped with SNMP support, but not 750 and 1000.
Power outlet block:

Without any special comments - maybe you can find something cheaper, easier. But a dozen "strangled raccoons" will not make the weather.
It remains to remember to decide whether a fan unit is needed in the cabinet? Expensive pleasure, especially when paired with a thermostat unit. However, we will attribute this to the specifics of the place / office.

We more or less figured out the closet, there were all sorts of “little things”, without taking into account which there will be annoying delays later:
* Screws with nuts for mounting equipment in the cabinet;
* Nylon non-opening ties for laying and fastening the cable (packs of 100 pieces, 100, 150, 200 mm long);
* Marking for the cable (adhesive sheets with a protective layer).
In fact, we got to the SCS itself. A very important "detail" is the cable, which will be used for wiring the SCS. Yes, again a call not to save. Good twisted pair is a good investment. We take Molex, unshielded UTP PowerCat 5e cable.

The cable is the core element of the PowerCat product line. The line is designed for use in high-speed telecommunication networks (eg GigaEthernet 1000Base-T).
We, of course, will come to subscriber sockets, and then what? Next - buy the required number of patch cords to connect workstations. Naturally, you need to think over the length, look at the office plan mentioned above. But that is not all. You also need a strainded cable (normal - solid). This is a special twisted pair, "soft", from which patch cords are made. After all, sooner or later you will definitely need a patch cord of a greater length than there are ready-made ones at hand (if at all by that time they remain). it will be necessary - as you wish) to make short - 30-50 cm, patch cords for crossing SCS lines and active equipment in the cabinet itself. Therefore, we "take a pencil" a couple more packages of RJ45 connectors, in common parlance - "chips". And packaging of rubber caps for them.It is better to take soft caps and with a slot for the "chips" retainer, and not with a "pimple" for the retainer.
We have almost reached the network interfaces on user computers, but subscriber sockets are still needed. Someone against such a wonderful thing as Molex OFFICE BLOCK 2xRJ45? ;-)

Compliance with the requirements of category 5e. The modules are designed for high-speed telecommunication networks. Possibility of cable entry from the sides, top or rear. As standard, the modules are equipped with dust shutters. Ease of labeling channels. The built-in magnet simplifies mounting the modules to metal surfaces. Possibility of fastening with screws. Cable fastening inside the module without cable ties. Free choice of connection sequence (568A/B). Connector type "KATT" facilitating installation. The kit includes mounting elements. .
Here it is necessary to determine the quantity. After all, there are single options. Again we take the plan of the office. There is another important point in determining the installation locations for sockets - it is advisable to add one or two additional SCS lines to each cabinet. One is just "just in case". What if the layout in the office changes a little or someone will need to connect a laptop? The second one is not bad to have based on the print server, for organizing network printing. It is very nice to have one or two network printers for your office or office that work without problems and whims of the owner (or Windows).
Do you think that's all? No. Another factor that is present in any office is forgotten - telephony. It's a good idea to think about this too: if telephones should be wired to some workplaces, then why not make a wiring in the general SCS? After all, the issue can be solved simply: throw a line or two to the necessary places, put an RJ-12 socket next to the RJ-45, even in one housing (unit). In the socket - DECT, for example, with several handsets, and in the cabinet we draw a line (lines) from the PBX - they can be put on sockets, neatly glued with Velcro inside and on the side. Lines from jobs - on them.
It seems like it's time to take on the cable channel and dowel-nails? Yes. It is time. But this is already clear to any handy man, we will not dwell on this for a long time. You just need to take into account the number of lines laid in the cable channel. And, of course, a small margin is needed. It is very good if the office has a suspended ceiling, the lines can be pulled behind it right to the workplace and lowered in a cable channel along the wall. When drawing lines, it’s a good idea to mark them (as well as sockets in the future). The easiest method is the first socket to the left of the door - No. 1, further in a circle.
After stretching the lines, you can start splitting the patch panel and sockets. Needless to say, this job requires accuracy and skill. It is at this moment that line marking will come in handy for us - if all the lines are split in order, then in the further operation of the SCS it will be possible to practically do without an installation map (layout), something like this:
Power socket
However, this card is still needed in the future. Will definitely come in handy.
When laying cables, you must follow a few simple rules (just simple ones, we will not delve into standards and other ISOs now):
* Do not severely bend, rub or step on the cable. Cable bending is allowed: during installation - 8, and, during operation - 4 radii of the cable itself;
* Do not lay lines near power lines: if necessary, lay them in parallel - at a distance of at least 20 cm;
* Crossing power lines is allowed, at a right angle;
* Mandatory testing by a cable tester.
Separately, about the last point. Remember the joke about the Japanese supply of something there? “Dear customers! We don't know why you need this, but we still decided to put in the boxes one defective chip for every ten thousand, according to your requirements. Yes, you can just split and forget. An experienced installer is not mistaken. However, a really experienced installer will definitely check, and not only the layout of the line, but also the quality.
Here we have reached the interesting moment. If we check a trifle with a simple and cheap tester, then to carry out tests and certify lines - no, it will not work:

Which exit? I really don't want to leave the issue of line quality unresolved. There are three options. The first is to buy a good tester, for example:
But, alas, we are very sorry for $6,000, even if it is for such a wonderful and necessary device.

It is a compact, handheld tool used for qualification, testing, and troubleshooting of coaxial and twisted-pair cabling in local area networks. The tester is recommended by leading manufacturers of information cabling systems for testing for system certification up to Class E inclusive. The high level of reliability, convenience and accuracy of the device provided him with one of the first places among the products of this class. For fast and high-quality testing of cable connections in an extended frequency range up to 350 MHz, technologies are used digital processing pulse signal.
The second option is to invite a familiar admin or installer who has such or a similar device. Of course, having previously bought a case of good beer. Half an hour of work, plus a beer evening in the pleasant company of a friend.
The third option is to officially invite specialists from a company that provides such services. and pay for these services. This is not so much, especially if you do not require a certificate on paper.
Remote workstations
Having "finished" (quotation marks because we must first still plan everything and make the necessary purchases and negotiations) with the work at the main office, we remember the warehouse and the store.
Now (in these notes) we will consider not a "tricky" solution like VPN, but the simplest one - organizing the connection of computer networks with subnets (workstations with a network) over a dedicated line. Effective, cheap and cheerful. By the way, allotments, of course, should be placed in a closet and connected to sockets, like telephones.

If the distance and, accordingly, the resistance of the leased line are small, you can try to install a pair of "bridges", for example, the already mentioned firms ZyXEL Prestige 841С and ZyXEL Prestige 841. Model "C" is "master", so this device is best installed at the head office. These are inexpensive VDSL devices, but they give the necessary results for our task. What ZyXEL says:
Depending on the type and condition of the cable, as well as on the distance, the Prestige 841 paired with the Prestige 841C provides the following data exchange rate:
In the direction to the subscriber - within the range from 4.17 to 18.75 Mbps
. in the direction from the subscriber - from 1.56 to 16.67 Mbps
. the total bandwidth of the line can reach 35 Mbps
Specifications:
VDSL Ethernet Bridge
. LAN connection at 15 Mbps up to 1.5 km
. Plug&Play, transparent to all protocols
. Working in pairs
. Desktop execution
. Non-volatile memory (Flash ROM)
. Size: 181 x 128 x 30mm
This option will give 18 Mb in each direction, ideally, of course. This is VDS.
When using Prestige 841 there is another plus. These devices have a built-in splitter, and we can get "free" telephony from a remote location. It is enough to plug into the “phone” socket on the one hand the telephone of the remote workplace, and on the other hand, connect the office mini-PBX.
If the VDSL bridges don't "stretch" the line, you need to look at other devices, xDSL. For example - something from the 79 series ZyXEL, SHDSL.

Optimization of the hardware and the use of advanced technologies have made it possible not only to reduce the dimensions of the device, but also to reduce the cost and improve functional characteristics. provide symmetrical connection at speeds up to 2.3 Mbps and can work on a leased 2-wire line both in point-to-point mode and as a client of an Internet provider hub.
Specifications:
. SHDSL router
. G.991.2 support up to 2.3 Mbps symmetrical
. Connecting networks or accessing the Internet over long distances
. Encapsulation PPPoA, PPPoE, RFC-1483
. TCP/IP Routing, Full NAT, Packet Filtering
. Support for IP Policy Routing, UPnP, connection redundancy
. Management via console, Telnet, Web, SNMP
The ideal speed is 2.3Mb over two wires. If you "charge" 4 wires, the speed will be correspondingly greater. However, these devices will cost a large amount - 400-500 dollars per pair. In any case, roughly speaking, the worse the quality of the line, the lower the speed and the higher the costs. However, we will postpone the tuning (tuning) of devices for the future, this is a separate conversation, especially since in the case of VDSL 841 this does not make too much sense at all. xDSL devices should be placed on a shelf in a closet. I told you it wouldn't be empty.
Internet connection

ZyXEL Prestige-660
A modern office is unthinkable without the Internet. To connect, we can use ADSL technology, for example - ZyXEL Prestige 660.
As ZyXEL describes this device:
Modem P-660R belongs to the fourth generation of ADSL modems and combines in one device the functionality necessary to connect an existing office or home network to the Internet: ADSL2+ modem, router and firewall. The modem will provide your office with a permanent Internet connection that works quickly and securely. Installation and maintenance of the P-660R modem is simple and will not cause any problems even for inexperienced users.
Main advantages of ZyXEL Prestige 660:
* High-speed Internet - up to 24 Mbps
* Reliable connection on problematic lines
* Free phone
* Permanent connection
* Does not require driver installation
* Works with W
Network technology is the minimum set of standard protocols and the software and hardware that implement them, sufficient to build computer network. Network technologies called basic technologies. Currently, there are a huge number of networks with different levels of standardization, but such well-known technologies as Ethernet, Token-Ring, Arcnet have become widespread.
To ensure consistent operation in data networks, various communication protocols for data transmission are used - sets of rules that the transmitting and receiving parties must adhere to for consistent data exchange. Protocols are sets of rules and procedures that govern how some communication is to take place. Protocols are the rules and technical procedures that allow multiple computers to communicate with each other when networked.
There are many protocols. And although they all participate in the implementation of communication, each protocol has different goals, performs various tasks, has its own advantages and limitations.
Protocols work at different levels of the interaction model open systems OSI/ISO. The functions of protocols are determined by the layer at which it operates. Several protocols can work together. This is the so-called stack, or set, of protocols.
Just as network functions are distributed across all layers of the OSI model, protocols work together at different layers of the protocol stack. The layers in the protocol stack correspond to the layers of the OSI model. Taken together, the protocols provide a complete description of the functions and capabilities of the stack.
Data transmission over a network, from a technical point of view, should consist of successive steps, each of which has its own procedures or protocol. Thus, a strict sequence in the performance of certain actions is maintained.
In addition, all of these steps must be performed in the same sequence on every networked computer. On the sending computer, actions are performed from top to bottom, and on the receiving computer, from bottom to top.
The sending computer, in accordance with the protocol, performs the following actions: Breaks the data into small blocks, called packets, with which the protocol can work, adds address information to the packets so that the receiving computer can determine that this data is intended for it, prepares the data for transmission through the network adapter card and then through the network cable.
The recipient computer, in accordance with the protocol, performs the same actions, but only in the reverse order: it receives data packets from a network cable; transfers data to the computer through the network adapter card; removes from the packet all the service information added by the sending computer, copies the data from the packet to the buffer - to combine them into the original block, passes this data block to the application in the format that it uses.
Both the sending computer and the receiving computer need to perform each action in the same way so that the data received over the network matches the data sent.
If, for example, two protocols break data into packets and add information (about packet sequencing, timing, and for error checking) differently, then a computer running one of these protocols will not be able to successfully communicate with a computer running the other protocol. .
Until the mid-1980s, most LANs were isolated. They served individual companies and rarely combined into large systems. However, when local networks reached a high level of development and the volume of information transmitted by them increased, they became components of large networks. Data transmitted from one local network to another along one of the possible routes is called routed. Protocols that support the transfer of data between networks over multiple routes are called routed protocols.
Among the many protocols, the following are the most common:
IPX/SPX and NWLmk;
The OSI protocol suite.
Ethernet is currently the most common technology in local area networks. More than 10 million local networks and more than 100 million computers with a network card supporting this technology operate on the basis of this technology. There are several subtypes of Ethernet, depending on the speed and types of cable used.
One of the founders of this technology is Xerox, which developed and created in 1975 a test Ethernet Network. Most of the principles implemented in the mentioned network are still used today.
Gradually, the technology was improved, responding to the increasing level of user requests. This has led to the fact that the technology has expanded the scope of its application to such a data transmission medium as optical fiber or unshielded twisted pair.
The reason for the start of using these cable systems was a fairly rapid increase in the number of local networks in various organizations, as well as the poor performance of local networks using coaxial cable. At the same time, there was a need for convenient and economical management and maintenance of these networks, which could no longer be provided by legacy networks.
Basic principles of Ethernet operation. All computers on the network are connected to a common cable called a common bus. The cable is a transmission medium, and any computer on the network can use it to receive or transmit information.
Ethernet networks use a packet data transfer method. The sending computer selects the data to be sent. This data is converted into short packets (sometimes called frames) that contain the source and destination addresses. The packet is supplied with service information - a preamble (marks the beginning of the packet) - and information about the value of the checksum of the packet, which is necessary to verify the correct transmission of the packet over the network.
Before sending a packet, the sending computer checks the cable, controlling the absence of a carrier frequency in it, on which the transmission will take place. If such a frequency is not observed, then it starts transmitting the packet to the network.
The packet will be received by all network cards of computers that are connected to this network segment. NICs control the destination address of a packet. If the destination address does not match the address of this computer, then the packet is rejected without processing. If the addresses match, then the computer will accept and process the packet, removing all service data from it and transporting the necessary information “up” through the levels of the OSI model up to the application one.
After the computer transmits the packet, it maintains a short pause equal to 9.6 μs, after which it repeats the packet transmission algorithm again until the necessary data is completely transported. The pause is needed so that one computer does not have the physical ability to block the network when transmitting a large amount of information. While such a technological pause lasts, the channel will be able to use any other computer on the network.
If two computers simultaneously check the channel and try to send data packets over a common cable, then as a result of these actions, a collision occurs, since the contents of both frames collide on a common cable, which significantly distorts the transmitted data.
After a collision is found, the transmitting computer is required to stop transmitting for a small random interval of time.
An important condition for the correct operation of the network is the mandatory recognition of a collision by all computers simultaneously. If any transmitting computer does not calculate the collision and conclude that the packet was transmitted correctly, then this packet will simply disappear due to the fact that it will be heavily distorted and rejected by the receiving computer (checksum mismatch).
It is likely that lost or corrupted information will be retransmitted by an upper layer protocol that works with connection establishment and identification of its messages. It should also be taken into account that retransmission will occur after a sufficiently long time interval (tens of seconds), which will lead to a significant decrease in the throughput of a particular network. That is why the timely detection of collisions is extremely important for the stability of the network.
All Ethernet parameters are designed so that collisions are always clearly identified. That is why the minimum length of the frame data field is at least 46 bytes (and taking into account the service information - 72 bytes or 576 bits). The length of the cable system is calculated in such a way that during the time that the frame of the minimum length is transported, the signal about the collision has time to reach the most distant computer on the network. Based on this, at a speed of 10 Mbps, the maximum distance between arbitrary network elements cannot exceed 2500 m. The higher the data transfer rate, the smaller the maximum network length (decreases proportionally). Using the Fast Ethernet standard, the maximum distance is limited to 250 m, and in the case of Gigabit Ethernet, 25 m.
Thus, the probability of successfully obtaining a shared environment directly depends on the network load.
The ever-increasing level of network bandwidth requirements led to the development of Ethernet technology, the transmission rate of which exceeded 10 Mbps. In 1992, the Fast Ethernet standard was implemented, supporting the transport of information at a speed of 100 Mbps. Most of the principles of Ethernet operation have remained unchanged.
Some changes have taken place in cable system. Coaxial cable was not able to provide a data transfer rate of 100 Mbps, so it is being replaced in Fast Ethernet by unshielded twisted pair cables, as well as fiber optic cable.
There are three types of Fast Ethernet:
The 100Base-TX standard uses two cable pairs at once: UTP or STP. One pair is required for transmitting data, and the second for receiving. These requirements are met by two cable standards: EIA/TIA-568 UTP Category 5 and IBM's Type 1 STR. 100Base-TX provides the possibility of full-duplex mode when working with network servers, as well as the use of only two of the four bundles of an eight-core cable - the remaining two pairs will be free and can later be used to expand the functionality of this network (for example, based on them it is possible organization of the telephone network).
The 100Base-T4 standard allows the use of category 3 and 5 cables. This is because 100Base-T4 uses four pairs of eight-core cable: one for transmit and one for receive, the rest can be used both for transmission, as well as for admission. Accordingly, both the reception and transmission of data can be carried out on three pairs at once. If the total bandwidth of 100 Mbps is distributed over three pairs, then 100Base-T4 reduces the signal frequency, so a lower quality cable is sufficient for normal operation. Category 3 and 5 UTP cables can be used for 100Base-T4 networks, just like Category 5 UTP and Type 1 STP.
The 100Base-FX standard uses multimode fiber with a 62.5 micron core and a 125 micron cladding to transmit data. This standard designed for backbones - fast Ethernet repeater connections within the same room. The main advantages of the optical cable were also transferred to the considered 100Base-FX standard: immunity to electromagnetic noise, an increased level of information security and increased distances between network devices.
For a long time, the Firewire interface (Firewire High Speed Serial Interface, also known as IEEE1394) was mainly used in processing streaming video. In general, for this he was originally designed. However, the highest, even by today's standards, throughput of this interface (400 Mbps) made it quite efficient for modern high-speed peripheral devices, as well as for organizing small high-speed networks.
Thanks to WDM driver support, the Firewire interface is supported by operating systems starting with Windows 98 Second Edition. However, native support for the Firewire interface was first introduced in Windows Millennium and is now supported in Windows 2000 and Windows XP. All operating systems except Windows 98SE also support network hot-plugging. If a Firewire controller is present on the system, Windows automatically installs a virtual network adapter, with the ability to directly access and modify the default network settings.
By default, the Firewire network supports the TCP/IP protocol, which is quite sufficient for solving most modern network problems, for example, the Internet Connection Sharing function ( sharing Internet) built into the Microsoft operating system.
Firewire provides a significant speed advantage over a standard 100BaseT Ethernet network. But this is not the main advantage of the Firewire network. More important is the simplicity of creating such a network, which is available to a user of not the highest level of training. It is also important to note the versatility and low cost.
The main disadvantage of a Firewire network is the limited cable length. According to the specification, for operation at a speed of 400 Mbps, the cable length should not exceed 4.5 meters. To solve this problem, various repeater options are used.
A few years ago it was developed new standard Ethernet -- Gigabit Ethernet. At the moment, it is not yet widely used. Gigabit Ethernet technology uses optical channels and shielded twisted pair as a medium for transporting information. Such an environment is capable of tenfold increase in data transfer rate, which is necessary condition for videoconferencing or the operation of complex programs that operate with large amounts of information.
This technology uses the same principles as earlier Ethernet standards. In addition, a network that is based on a shielded twisted pair can be implemented through the transition to Gigabit Ethernet technology by replacing network cards and network equipment that are used in the network, 1000Base-X contains three physical interfaces at once, the parameters and characteristics of which are listed below:
The 1000Base-SX interface defines lasers with an allowable radiation length in the range of 770-860 nm, the transmitter radiation power in the range from 10 to 0 dBm, with an existing ON / OFF ratio (signal / no signal) of at least 9 dB. The sensitivity of such a receiver is 17 dBm, and its saturation is 0 dBm.
The 1000Base-LX interface defines lasers with an allowable emission length in the range of 1270-1355 nm, transmitter emission power in the range from 13.5 to 3 dBm, with the existing ON / OFF ratio (signal / no signal) not less than 9 dB. The sensitivity of such a receiver is 19 dBm, and its saturation is 3 dBm.
1000Base-CX is a shielded twisted pair cable designed to carry data over short distances. All four pairs of copper cable are used for data transportation, and the transmission rate over one pair is 250 Mbps. Gigabit Ethernet is the fastest LAN technology available today. Soon enough, most networks will be based on this technology.
Wi-Fi technology wireless communication. This name stands for Wireless Fidelity (from English - wireless accuracy). Designed for access at short distances and, at the same time, at sufficiently high speeds. There are three modifications of this standard - IEEE 802.11a, b and g, their difference from each other in the data transfer rate and the distance over which they can transmit data. The maximum operating speed is 11/ 54/ 320 Mbps, respectively, and the transmission distance is about 100 meters. The technology is convenient in that it does not require much effort to connect computers to a network, and allows you to avoid the inconvenience that occurs when laying a cable. Currently, services can be used in cafes, airports, parks, etc.
USB network. Designed mainly for laptop users, because. in the absence of a network card in a laptop, it can be quite expensive. The convenience is that the network can be created without the use of network cards and hubs, versatility, the ability to connect any computer. Data transfer rate 5-7 Mbit / s. Local network through electrical wires. 220V. Electrical networks cannot be compared with local and global networks. There is an electrical outlet in every apartment, in every room. Dozens of meters of cables can be stretched around the house, connecting all computers, printers and other network devices. But then each computer will become a "workplace", permanently located in the room. To move it means to shift the network cable. You can install an IEEE 802.11b wireless network at home, but there may be problems with signal penetration through walls and ceilings, and besides, this is unnecessary radiation, which in modern life so enough. And there is another way - to use the already existing electrical wires and sockets installed in the walls. The only thing that is required for this is the appropriate adapters. The network connection speed through electrical wires is 14 Mbps. The range is approximately 500 meters. But it should be borne in mind that the distribution network is three-phase, and one phase and zero are supplied to the houses, evenly loading each of the phases. So, if one user is connected to one phase, and the second to another, then it will not be possible to use such a system.
A comparative analysis of local area network technologies is presented in Appendix B.
IN modern world LANs have become more than just a necessity - they're actually essential to achieving a good level of productivity. However, before you start using such a network, you should create and configure it. Both of these processes are quite difficult and require maximum concentration, especially the first of them. A poorly designed and configured LAN will not work at all, or it will not function at all as it should, so creating a local network should be the focus of attention for the person doing it.
What is a local network
Typically, creating similar systems communication is caused by the need to share data by users who work on remote computers. LAN not only allows for near-instantaneous exchange of information and simultaneous work with files, but also allows you to remotely use network printers and other devices.
A local network is a complete set of software and hardware resources aimed at creating a single information space. In fact, this is a number of computers located at a distance from each other and connected by a communication line - a cable. The main difference between a LAN and other types of networks is the short distance at which workstations are located.
Pre-project preparation and design
Before you create a local network, you must first design it, that is, plan the process of its creation. This stage is one of the most significant, since the LAN includes a huge number of components and nodes.
Initially compiled technical task based on primary data, identifying several points:
- Functions and tasks of the LAN.
- Selected topology.
- List of available equipment.
Once you have these points in mind, you can start designing. The project itself should contain LAN schemes, network equipment placement points, a list of required software and hardware.

A local area network is a complex mechanism, but if it is designed correctly and the equipment is selected in accordance with the requirements, then the likelihood of problems in the operation of the communication mechanism becomes minimal.
Required Hardware
There is a list of equipment without which no LAN can function. It includes:
- Data lines. The most commonly used coaxial cable and optical fiber. In this case, the length of the coaxial cannot exceed several hundred meters, however, if it is necessary to extend the network over long distances, special repeaters are used - signal repeaters that do not allow it to fade.
- Communication equipment: network cards (devices that perform duplex exchange of information between a computer and a data transmission medium), hubs (they divide the network into separate segments, structuring the network physically), routers (take on the choice of the packet transmission route), switches (logically divide the LAN into segments, combining several physical circuits), repeaters (provide signal recovery, allowing you to increase the length of the transmission medium), transceivers (amplify the signal and convert it to other forms, allowing you to use different data transmission media).
List of software
No LAN is complete without software. Required Programs for local network include:
- Operating systems of work nodes. The most commonly used operating system remains Windows 7, although Windows XP is also not losing ground.
- Network operating systems installed on servers are the basis of the LAN, since it is impossible to set up a local network without them. Exactly these software take control of all data flows between the main and secondary nodes, providing the possibility of collective access to network resources. As a rule, the operating systems of Microsoft Corporation are used: Windows Server 2003 or 2008.

- Network services and applications that enable users to access deleted files, print documents on a network printer, view networked work sites, and send emails. The implementation of such services is carried out using software.
Creation and installation of a LAN
Installation and commissioning work takes the most time, since it is necessary to create a local network in several stages:
- Before starting the installation of communication lines and switching devices, you must first prepare the room.
- Next, you can lay the cable, as well as install the necessary equipment.
- Devices of the server and workstations should be connected to the cable communication line.
- After that, the software is installed and configured.
Installation of cable and equipment has a number of features, therefore, if there are difficulties with how to connect a local network, it is better to entrust this issue to specialists.
Joining two computers in a LAN
In some cases, it may be necessary to combine two computers into one network, for example, to create a common information space. This is not very difficult to do if you follow a certain algorithm of actions:
- If necessary, install network adapters in both computers, not forgetting the drivers.

- Purchase a crimped network cable for connection. If you have the necessary knowledge and skills, crimping can be done on your own - the local network of two computers will not become worse quality from this.
- Connect both workstations with a communication line.
- Set up the LAN in a specific order.
Algorithm for setting up a local network between two computers for Windows 7
- Select the "Start" menu, then, by right-clicking on the "Computer" icon, enter the "Properties" submenu.
- You need to find in the list "Computer name and domain", and then select the item with the change in settings.
- The working name of the computer must be changed by clicking on the appropriate icons.
- The group name should remain unchanged - "Workgroup", but the computer names are changed to "pc1" and "pc2" for the first and second subscriber, respectively.
- You can now click OK and restart your computer.

In most cases, you may want to give each host a unique IP address:
- From the Start menu, select Settings and then Network Connections.
- Right-click to open the "Properties" submenu next to the "Local Area Connection" icon.
- In the "General" tab, select "Properties" of the item "Internet Protocol".
- Make the line "Use the following IP address" active and enter the value 192.168.0.100. After that, save the changes made.
Local network and internet
Work nodes connected in a LAN can be connected to the Internet. A local network, to which the Internet can be connected in two ways, will work at a speed divided in two.
The first way to connect is to use a router, which is assigned an identifying IP address. And in the second case, you can use a wireless connection.
In this case, the local network is the interaction of two computers, master and slave, so the IP address is written in the gateway of the main one, previously connected to the worldwide network.

If the LAN is based on the use of a server, each work station must have an individual IP address, and a proxy server is specified in the browser settings through which Internet access is provided.
Wireless LAN
A wireless local area network is a type of LAN that uses high-frequency radio waves to transmit information. WLAN is an excellent alternative to the conventional cable communication system, having a number of advantages:
- Improving labor productivity. WLAN makes it possible to use the Internet without being tied to one room. You can freely change your location without losing your internet connection.
- Easy installation and configuration, financial savings and reliability - all these factors are due to the absence of a cable communication line.
- Flexibility. Installing a wireless network is real where there is no way to stretch the cable.
- Possibility of expansion. Network scalability is greatly simplified thanks to wireless network adapters, which can be installed on any worker node.
WLAN has a certain range, which depends on the characteristics of the network devices and the noise immunity of the building. As a rule, the range of radio waves reaches 160 m.
Necessary equipment for creating a wireless LAN
An access point is used to connect other workstations to the network. This device is equipped with a special antenna that controls duplex data transmission (sending and transmitting) using radio signals. Such a point can transmit a signal at a distance of up to 100 m indoors and up to 50 km in an open area.

Access points significantly expand the computing power of the entire communication system, allowing users to freely move between each of them without losing connection to the LAN or the Internet. In fact, these radio points act as hubs, providing a connection to the network.
Using access points allows you to scale up your entire wireless LAN by simply adding new devices. The number of subscribers that one radio point can withstand generally depends on the network load, since the traffic is divided equally between each of the users.
Wireless LAN: Windows 7 Setup Flow
First you need to prepare an ADSL modem with WiFi technology, as well as client points with connected to them wireless adapters. After that, you can start building a wireless LAN:
- Connect the modem to the electrical network.
- Run the WLAN setup wizard on the client device.
- Select the SSID from the list of found wireless networks.
Access point setup:
- The first step is to configure the TCP/IP protocol properties by specifying the IP address and subnet mask.
- Then enter the value DNS servers, since it is not possible to fully configure the local network without this parameter. In most cases, it is enough to make the automatic assignment of the DNS address active.
- It is also mandatory to configure the parameters of the wireless network itself, in which security is important.
- At this stage, you need to configure the Internet connection and filtering for the Windows 7 firewall.
- And lastly, the wires are connected and the WLAN network is tested.
To create an optimal information space, you can combine types of networks - cable and wireless, allowing you to use the advantages of each of them for the benefit of the enterprise. However, it is important to remember that in our time, it is more and more used precisely wireless networks WLAN, which has all the advantages of cable networks and is devoid of their disadvantages.
After completing the creation and configuration of the local network, it is important to provide for its administration and the possibility of maintenance. Even if the LAN is installed perfectly, during its operation various hardware or software malfunctions are almost inevitable, which is why maintenance should be regular.